Strategic and Financial Advisory
A multi-dimensional transformation taking place today is fundamentally changing the ways in which electric, gas, and water utilities plan, operate and interface with their customers. Our clients are feeling the impacts from increased penetration of distributed energy resources, the wide variety of options for smart grid technologies, an evolving role for natural gas, complex regulatory requirements, and expanding customer expectations for new and innovative products and services.
Through our consulting assignments, MCR helps our clients navigate challenges and opportunities they face and understand them from an investor’s perspective and create opportunities to increase value for their customers, shareholders and other key stakeholders. We achieve this by developing customized strategies that are both manageable and executable.
Key Staff

Sam Brothwell, Vice President
Sam is Vice President of Strategic and Financial Advisory. Sam’s background includes a decade in utility industry corporate planning and investor relations, fifteen years on Wall Street as a senior equity and credit financial analyst and nearly a decade as a utility and pipeline investor. His background includes electricity, natural gas, and renewable energy. Sam has worked extensively with federal and state policy makers as well as non-government organizations involved in the energy and utility sectors, and he has spoken at numerous industry conferences and investment forums.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
Insights
- Why Can’t We Be Friends? Gas and Electricity Can Meet Energy Challenges Together
- DeepSeek, or Deep Fake? Data Center Challenges and Opportunities for the Power Industry
- Utility Cost Management—A Strategic Approach
- Utility Headwinds Call for Smart Cost Management
- The fallout from the SVB event and how utility financial professionals should respond (Point-of-View)
- Stove wars—is natural gas part of the problem or part of the solution? (white paper)
- Cutting Carbon and Adding Renewables May Not Win ESG Points
- Now for the Hard Part – Growing Your Utility without the Triple Two’s (white paper)
- Investor Perspectives on Natural Gas Utilities
Key Staff
Participating in a National Standard Practice Manual Stakeholder Process
Recently, staff of MCR’s Regulatory Services practice joined staff from the Energy Products and Services practice in participating in a National Standard Practice Manual (NSPM) stakeholder process as an independent subject matter expert. In the brief case study, MCR shares perspectives on the cost-effectiveness test development process, mandated by the jurisdiction’s regulatory body, from our utilities-only lens.
Why Can’t We Be Friends? Gas and Electricity Can Meet Energy Challenges Together
Utilities today are challenged to deliver reliable, resilient, affordable, and clean energy against a backdrop of high interest rates, inflation, and increasingly hostile weather. Rather than “gold-plating” to address peak loads and tail risks, utilities might better serve their customers by working together to optimize use of built-and paid-for gas and electric delivery infrastructure.

Ian Richter, Consultant
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
The Growing Imperative for Natural Gas Energy Efficiency – American Gas Foundation
The American Gas Foundation (AGF) engaged MCR to evaluate the full range of current and future potential benefits that could accrue from natural gas utility energy efficiency (EE) programs, including 1) the current state of gas utility EE cost-effectiveness, and 2) perspective potential future benefits. The report provides an in-depth survey of existing natural gas utility EE programs as well as potential future program approaches and incentive strategies. The study also highlights opportunities to leverage indirect and non-energy benefits stemming from optimal and efficient use of natural gas delivery infrastructure.
DeepSeek, or Deep Fake? Data Center Challenges and Opportunities for the Power Industry
Artificial intelligence–and the power-hungry data centers that run it—dominated utility investor dialog last year. The power sector has decades of experience with shiny new sources of electricity demand—and the scars to prove it. Supply is being built, and the data centers are coming…but it’s fair to ask if they’ll all stick around.
Investor Perspectives on Natural Gas Utilities
The American Gas Association (AGA) and the Canadian Gas Association (CGA) commissioned MCR Performance Solutions LLC (MCR) to update and enhance their 2022 study, “Investor Expectations on North American Gas Utilities.” MCR found that while the gas utility industry’s underlying commercial foundation remains solid, regional policy challenges coupled with rapidly growing energy demand (and the urgent imperatives of affordability, security, resilience, and reliability) suggest there is potential in considering new commercial avenues—avenues that can both sustain a mature industry and align business strategies with important public policy and social objectives.
Read the Investor Perspectives on Natural Gas Utilities
Is your Nuclear Plant Capitalizing All the Costs you’re Entitled to?
Reducing O&M costs is one of the highest priorities for nuclear generation executives today. Often overlooked, however, are project expenditures. A nuclear generation plant incorporates numerous interdependent pieces of equipment and components, and it can be difficult to identify whether items constitute discrete units of property (UoP), major components or something else.
Read the Nuclear Generation Services Insight
Cash Working Capital and Lead-Lag Studies
In the evolving regulatory landscape, utilities across the electric, gas, and water sectors are facing increasing scrutiny from regulators who are demanding more detailed calculations of cash working capital. This requirement reflects a broader push for greater accuracy in the financial management of utilities, ensuring that rates charged to customers are fair and reflective of actual operational needs. Our team understands the complexities of cash flow management and the regulatory environment, ensuring that your utility’s cash working capital is calculated accurately and efficiently.
Read the Cash Working Capital and Lead-Lag Studies Insight>>>

Nikhil Tarlapally, Lead Consultant

John Simpsen, Lead Consultant
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Dylan Robideaux, Lead Consultant
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Ted Konstantino, Associate Consultant

Wale Adeyinka, Lead Consultant
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
Rate Case Services
MCR develops solutions to key issues facing utility executives. MCR works with you and your stakeholders to provide solutions that work in your regulatory jurisdictional environment. Our industry experts assist electric, natural gas and water companies.
Read the Rate Case Services Insight>>>
How MCR Helped an Electric Utility Develop and Implement a New Cost of Service Model
Background
The electric IOU Public Service Company of New Mexico (PNM) faced a number of challenges with its cost of service model. Intervenors struggled to understand the model during rate cases, slowing down the regulatory process. The model wasn’t user friendly and was difficult to master. In addition, it was proprietary, so if changes were required, PNM had to go back to the vendor to implement them. A new cost of service model was needed to meet the utility’s internal needs and make the regulatory process more efficient. So PNM reached out to MCR, both for our customizable cost of service model and our specialized expertise.
Approach
MCR’s Cost of Service Tool (COST™) is unique to the industry and features transparent formulas, an automated import tool, and an integrated rate design module. Further, the COST™ license allows for companies to take full control over the model once implementation is complete if they desire.
PNM chose to retain MCR to implement the COST™ model and assist them with their first rate case after implementation. Our team developed a 12-week implementation timeline to adapt the modular COST™ model for PNM, using the company’s prior cost of service study as a guide. This assured them that when the COST™ model was finalized it would fit within the regulatory guidelines required by their jurisdictional authority. Throughout the implementation process, MCR compared the COST™ model with prior studies to ensure that the outputs of the two models were similar. Where differences were found, we worked with PNM to determine how they would be addressed in the new model.
For greater efficiency, the COST™ model’s rate design module was implemented at the same time as the cost of service portion. MCR worked with the PNM team to adapt their inputs to the COST™ model’s data import tool, so that data in subsequent runs of the model could be inputted quickly and accurately. Throughout the process, MCR held frequent check-in meetings with our clients, keeping them informed, soliciting their feedback, and providing them with hands-on training to ensure that they were familiar with the model and could run it on their own. Documentation was also provided, customized to PNM’s version of the COST™ model.
During the rate case, PNM asked that MCR work on an accelerated timeline, developing the COST™ model for the requested test year and designing the proposed rates in just one month. Our team updated the COST™ model and its attached rate design module with current and prospective data. We ran multiple studies for PNM and worked with our clients and their leadership team to develop multiple rate design scenarios. We assisted in drafting testimony and worked with our clients to prepare all the exhibits needed for filing and handled subsequent data requests once the case had commenced. We also provided training for the intervenors in the case, enabling them to develop alternative studies and rate designs within the same model.
Results
MCR’s COST™ model was accepted by PNM’s commission, and the sole intervenor’s objections to the model were rejected. PNM called the COST™ model “very easy to use,” adding, “We were able to pull the numbers seamlessly and easily.” Intervenors found the models easy to understand as well. Once trained, our clients had a few questions for clarity, but they were able to make the necessary changes on their own.
PNM has now retained MCR for a subsequent rate case. We updated the COST™ model with new enhancements that have been added since their first rate case. Using the training provided by MCR, PNM is completing the COST™ model and its rate design module on their own this time, calling on our team to assist as needed.
Download Client Story as a PDF >
No Time To Waste In Filing for Transmission Rate Incentives
The Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) is undergoing the most ambitious transmission expansion in its history. This process, called Long-Range Transmission Planning (LRTP), consists of four project portfolios, or tranches. In July 2022, the MISO Board of Directors approved the first tranche of transmission solutions developed to provide reliable and economic energy delivery to address future reliability needs. Tranche 1 includes 18 projects, also referred to as LRTPs, with an estimated cost of $10.3 billion. These 18 projects are in the MISO Midwest Subregion and include more than 2,000 miles of transmission lines.
Download the Transmission Hot Topic
Case Study: Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for EV Programs
Utility Cost Management—A Strategic Approach
Cost management and budgeting in the utility industry are often based on prior year actual numbers and activity, without questioning why specific line items need funding, or evaluating the risk of not funding or carrying out a particular project or activity in a given year. MCR’s nuclear practice has developed a proprietary, strategic approach to facility-wide cost management, capital project evaluation, and capitalization vs expensing decisions with demonstrated savings in the hundreds of millions of dollars. This strategic approach is outlined in our most recent whitepaper.
Lessons Learned from the Rate Case Process
As utilities find themselves in need of increased revenue, it is important to evaluate lessons learned from prior rate case proceedings so the next rate case will be more successful. This paper focuses on lessons learned in four areas: 1) understanding the regulatory process, 2) employing stakeholder engagement, 3) confirming data integrity, and 4) leveraging staff’s experience to ensure rate case needs are met.
How MCR Helped a Southern IOU Develop a Green Energy Tariff as Part of Securing Renewable Load
Background
A Southern vertically integrated electric company was signing a power purchase agreement (PPA) to secure renewable load. As part of that process, they wanted to know whether a specific tariff for renewable energy would be acceptable to both customers and regulators, and whether it made business sense for the company to pursue for this renewable load. The company needed help investigating green tariff options. Having used MCR to conduct other research and analysis projects, they called on MCR to research and propose suggestions for a green tariff.
Approach
Our client wanted to understand what tariff option would be best for its customers to use under this renewable PPA. So MCR conducted an extensive study of the markets for green tariffs and renewable energy credits (RECs) locally and regionally, leveraging research already completed by the utility. We developed a presentation for senior management describing the basics of RECs and green tariffs, as well as green tariff offerings utilized by utilities in their region and in the rest of the United States.
MCR also researched the local jurisdictional authority, examining the dockets, testimony, and orders for other local utilities that had already implemented green tariffs. This information was consolidated to give a complete but summarized view of the regulatory climate for green tariffs. For the utility’s jurisdiction, we were able to show which green tariff options had been successfully implemented, the outlook given by the regulators and their staff on green tariff options, how the local REC market would affect the choice made by the utility, how RECS were accounted for, and what customers were specifically looking for from a green tariff.
Based on this research, we focused on four types of green tariffs that are commonly used and accepted by regulators and customers.
- Green Power Products. The utility procures renewable energy for customers who select this option, either through new construction or on the open market. These customers pay a premium on top of their normal bill to cover the cost of both the renewable energy and the administrative costs of the program.
- Sleeved PPA Services. Utility customers enter into a PPA with a renewable energy provider. The utility handles the transfer of money and energy to and from a renewable energy project on behalf of the buyer. If the energy does not cover the buyer’s needs, the utility is responsible for supplying the additional power. The customer either pays a premium or receives a discount on their normal electric supply charges, depending on the terms of the
PPA. - Subscription Services. The utility procures renewable energy for its customers, either through new construction or on the open market. The procured energy is divided into blocks of capacity or facility output, which are sold to customers at a fixed price. Customers receive a credit on their utility bill for energy provided by their subscribed number of blocks.
- Virtual PPA Programs. This type of tariff is normally utilized by renewable developers. Customers enter into multi-year bilateral energy contracts to pay for the energy produced by the developer at a fixed price. The developer then sells the energy on the open market. The difference between what the energy was sold for and what the customer paid for the energy is either credited to or subsequently charged to the original customer.
Results
MCR recommended that this IOU move forward with a green power product, as these products are the easiest to implement, are most accessible to all customers, and have a proven track record in our client’s jurisdiction. The client accepted MCR’s recommendation and is expected to file the green tariff once other regulatory priorities are resolved.
Download Client Story as a PDF >
Utility Headwinds Call for Smart Cost Management
As third quarter earnings reports begin, utility results will be scrutinized for hints of slowing growth against a backdrop of higher interest rates and upward pressure on labor and other costs. The likelihood of “higher for longer” points up a need for a strategic and sustainable approach to cost management.
SECURITIZATION: A Valuable Tool for Cost Recovery Opportunities Outside a Normal Rate Case
In recent years, a flurry of legislative activity has addressed utility securitization. Seventeen states have passed legislation offering securitization options to their electric utilities in the last decade, and several other states have proposed similar legislation. Securitization, while not a new concept, has been a successful tool for utilities to improve cost recovery while saving customers money on their electric bills. In this paper, we analyze trends in securitization legislation and detail the options that may work for your utility.
Read the securitization white paper>>>
Five Key Strategic Considerations for the Utility Regulatory Process
Of the many business functions unique to utilities, the process of setting rates is probably the most arcane and least understood by those outside the industry. While developing a financial model in support of a given tariff is relatively straightforward and formulaic, implementing it in the rate-setting process comes with myriad subtleties. The state-level regulatory context typically involves a quasi-judicial process and multiple constituents with different and often competing motivations. This paper examines some strategic considerations associated with the rate-setting process, highlighting the importance of the utility’s regulatory relationships.
Transmission Investment Analysis
With the recent surge in transmission investment being proposed, our cooperative, public power, and independent developer clients are all asking the same two questions: I know investing in transmission tends to be good, but how much value does it really provide for our members/ customers/owners, and how do I manage the risk?
Download Transmission Investment Analysis Insight
Modern Electric Vehicle Rate Design Options
Electric vehicle (EV) sales increased dramatically in 2022, with more than 750,000 new all-electric cars registered in the United States – a 55% increase over 2021 sales. Although forecasts vary widely, many analysts expect strong acceleration in EV adoption. Some analysts forecast EVs could represent 50% of total U.S. passenger car sales by 2030.
If growth rates to 2030 are even close to those projected, electric distribution systems will face massive challenges as most are not equipped to handle the increased load. One effective action utilities can take is to design tariffs to manage the charging load, fairly recover costs, and empower customers with flexible rate alternatives. To better understand these pricing solutions, we identified and analyzed several modern EV rate designs and explored how to implement them.
This white paper is Part 2 of the series, “Is Your EV Strategy Ready – Yet?
Modern Electric Vehicle Rate Design Options
Electric vehicle (EV) sales increased dramatically in 2022, with more than 750,000 new all-electric cars registered in the United States – a 55% increase over 2021 sales. Although forecasts vary widely, many analysts expect strong acceleration in EV adoption. Some analysts forecast EVs could represent 50% of total U.S. passenger car sales by 2030.
If growth rates to 2030 are even close to those projected, electric distribution systems will face massive challenges as most are not equipped to handle the increased load. One effective action utilities can take is to design tariffs to manage the charging load, fairly recover costs, and empower customers with flexible rate alternatives. To better understand these pricing solutions, we identified and analyzed several modern EV rate designs and explored how to implement them.
This white paper is Part 2 of the series, “Is Your EV Strategy Ready – Yet?
Cutting Carbon and Adding Renewables May Not Win ESG Points
Switching from coal to natural gas and renewables has made the power sector a leader in cutting US carbon emissions. But adherence to a strict environmental, social, and governance (ESG) diet would deny capital to the very sector that’s doing the most good.
With Criticality achieved, the Nuclear Industry is more important than ever
Nuclear generation is the largest and most reliable source of carbon-free, around-the-clock electricity. While this idea is gaining environmental and mainstream recognition, we believe more needs to be done to economically compensate nuclear for its increasingly crucial role in maintaining grid reliability.
Energy Efficiency: Today’s Silver Bullet For Gas Utilities
Now more than ever, MCR has found in its current and recent work that gas utility energy efficiency products and services are a strategic opportunity, perhaps a strategic imperative, for local distribution companies (LDC). Gas energy efficiency is an impactful tool in the LDC’s load growth and retention toolbox. Also, as the influence of ESG on cost of capital, shareholder activism, and state and federal policy increases, gas energy efficiency is a big part of improving ESG scores and demonstrating a positive impact on energy and environmental justice priorities.
Point of View: Gas Energy Efficiency for Strategic Load Growth & Retention
It is time for gas companies to ask themselves a critical question: Can gas energy efficiency programming be used as a strategic opportunity to grow and retain load? Customer-funded natural gas energy efficiency (EE) spending via utility EE programs has risen from approximately $300 million per year in 2006 to over $1.5 billion today. Largely as a regulatory compliance obligation. The current focus on electrification, and other market and political dynamics, create a strategic imperative for gas utilities to reexamine energy efficiency products and services.
In this Point of View piece, exclusively for gas utilities, MCR’s Ed Schmidt discusses use of energy efficiency to maintain and even grow natural gas load.
Cooperatives Gaining Substantial Benefits for Renewable Investments
The Inflation Reduction Act has designated billions of dollars to support cooperative development of renewables. Our analysis show how coops now have viable options to develop their own projects
Download the Cooperatives Benefits white paper
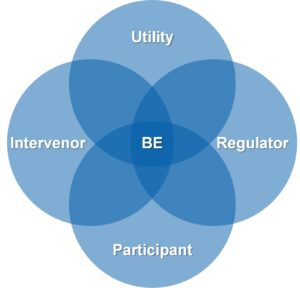
Beneficial Electrification: A Smart Strategy Makes the Difference
Utilities nationwide are launching beneficial electrification (BE) initiatives, both to respond to market and policy evolutions and to enhance the growth of their electric business. Success begins with a well-thought out strategy.
Download Beneficial Electrification Insight.
Benefical Electrification: A Smart Strategy Makes the Difference
Utilities nationwide are launching beneficial electrification (BE) initiatives, both to respond to market and policy evolutions and to enhance the growth of their electric business. Success begins with a well-thought out strategy.
Download Benefical Electrification Insight.
Reconcile Safety & Reliability Cost
MCR assists nuclear plants by teaching techniques to prepare robust business cases with creative alternatives, quantifying reliability and financial risk. With this information, the Executive Review Team is empowered with previously unavailable insights to confidently make the best decisions.
Cost Reduction through Risk-Informed Budgeting
As part of an overall effort to inject more rigor into the development of their Operations & Maintenance (O&M) budget, a top-10 integrated utility in the Southwest sought to engage a firm with extensive experience in providing consulting services in zero base budgeting (ZBB) for utilities.
Developing a Strategic Business Plan for a Cooperative (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“This Transmission Business Strategy was a great opportunity to get in front of our Board of Directors and our senior staff and do an education piece on the key industry issues, but also to inform them of our transmission strategies. I’m very happy with how it turned out.”
—Vice President of Transmission, Cooperative
Background
A Midwestern cooperative was faced with increased interconnection requests and wanted to ensure that its transmission OATT and rate formula was equitable and in line with general FERC and industry practices. Moreover, the client wanted to ensure that its transmission-related costs and appropriate return were recovered. Ensuring the cost recovery formula was consistent with industry practices was particularly important given the company was faced with multiple staff retirements, including accounting positions who would be responsible with updating the formula rate.
In addition, the company wanted to develop a Transmission Business Plan to transition it from a company that largely views the Transmission function as an operational necessity to one that views Transmission as a business that actively can contribute substantial revenue and value for its member-owners. This strategic transition was particularly timely given the transmission business function had new management and staff.
Solution
In Phase 1, MCR reviewed the clients’ interconnection and grandfathered agreements and identified ways to revise its interconnection policies to ensure alignment to typical RTO policies. We then conducted a transmission formula rate review to identify potential improvements in how costs are recorded and how transmission revenue can be optimized. In Phase 2, MCR led a senior client working team through multiple meetings to develop a five-year Transmission Strategic Business Plan. Our approach included identifying and prioritizing key transmission industry issues/trends and methods for creating member value, and developing a vision, objective areas and strategies. It also included identifying transmission project opportunities for improving member reliability and creating financial value. We used MCR’s Transmission Project Evaluation Tool™ to conduct a financial analysis of one potential project. We also incorporated investment metrics from MCR’s Proprietary Transmission Investment and Load data base into the analysis to compare the client’s rate of transmission investment to its peers. The results of the Transmission Strategic Business Plan, including an education session on key industry issues were presented to the senior management team and the Board.
Results
The client made changes to its OATT and interconnection policies to more closely align with continuing changes to standard industry approaches in order to proactively address any potential interconnection customers’ issues. Based on the transmission formula rate review, the company is considering making changes to how some costs are recorded, thus improving its annual transmission revenue requirement (ATRR) by 5%. The client is moving forward with its Transmission Business Plan, including implementing about 18 high priority strategies that address the top issues, and create value for its members through reliability improvements, better access to additional resources, or enhanced transmission revenue from third parties. Lastly, the client management, Board and staff are better educated on industry issues, allowing for improved decision-making, consistent with their vision and strategies.
FERC Filing Support – Supporting Public Power and Cooperatives in Transmission FERC Filings (Brochure)
MCR supports clients in transmission FERC filings in:Transmission incentive rate filings, Section 205 rate filings involving cost of capital testimony and formula rate support, and intervention and settlement support.
You must be logged in
Stove wars—is natural gas part of the problem or part of the solution? (white paper)
Natural gas has emerged as arguably the world’s most critical source of energy, but the industry seems to be battling for its own survival in the face of environmental activism and local attempts to ban its use. In our view, the gas industry needs to emphasize the role it plays not only in the transition to cleaner fuels, but in assuring the reliable delivery of all forms of energy, including electricity.
Strategic Business Planning for Transmission Owners
MCR works with clients to develop strategic business plans for transmission owners that set them up for success. These actionable plans address key transmission issues and help utilities transition to running transmission as a business rather than merely an operational necessity.
Read Strategic Business Planning for Transmission Owners
The fallout from the SVB event and how utility financial professionals should respond (Point-of-View)
Over the past few weeks, business news headlines have been overwhelmed by echoes of the 2008 and 2020 financial crisis. Utilities are highly capital-intensive and rely on banks, particularly for short-term financing; should they be concerned about recent events?
Now for the Hard Part – Growing Your Utility without the Triple Two’s (white paper)
U.S. utilities have enjoyed a decade of capital investment that is delivering greater reliability and efficiency for customers, strong returns for shareholders and lower environmental impacts for all. Looking ahead, the industry faces a generational investment opportunity in a transitioning energy world, but in our view, execution risk is rising. Why?
Client Stories
MCR’s Strategic and Financial Advisory practice works with electric, natural gas and water utilities. They include Investor-Owned utilities, Generation and Transmission Cooperatives and Municipal and Public Power companies.
Please visit our website in the coming months to receive updates on our latest client success stories.
Insights
What we do
Finance and Investor Relations
MCR helps our clients better understand capital markets and what’s driving their company’s stock. We provide expert analysis on ownership changes, valuation, dividend policy, peer ownership, analyst recommendations, and market trends. We provide informed investor targeting and activist surveillance. We support investor and board communications ranging from press releases to presentation materials to board and investor events, helping to clearly communicate strategy, goals, and execution.
Corporate Planning
MCR evaluates strategic options ranging from business line and product ideas to merger, acquisition, and divestiture proposals as well as financing alternatives from a non-transactional point of view. We help our clients evaluate potential changes to business models and regulatory compensatory systems and structures as the utility landscape evolves. We help develop cost-effective solutions to meet changing consumer expectations, regulatory and policy initiatives, rising costs, and incorporation of new technologies and business practices.
Natural Gas and Electric Strategies
We work with senior management to evaluate specific projects or business and regulatory tactics, analyze legislation and regulatory / policy actions. We provide assistance in developing strategic positioning for natural gas utilities, their role in decarbonization and support for electric utility reliability. For electric utilities we offer assistance in addressing electrification, EV’s, renewables and storage.
Regulatory and Finance
We partner with MCR’s Regulatory practice to provide superior solutions in regulatory and finance, advising on equity and credit market capital formation, cost of capital, performance-based ratemaking, and financial communication. We provide cost of capital analysis and expert witness testimony.
Strategic and Financial Advisory
A multi-dimensional transformation taking place today is fundamentally changing the ways in which electric, gas, and water utilities plan, operate and interface with their customers. Our clients are feeling the impacts from increased penetration of distributed energy resources, the wide variety of options for smart grid technologies, an evolving role for natural gas, complex regulatory requirements, and expanding customer expectations for new and innovative products and services.
Through our consulting assignments, MCR helps our clients navigate challenges and opportunities they face and understand them from an investor’s perspective and create opportunities to increase value for their customers, shareholders and other key stakeholders. We achieve this by developing customized strategies that are both manageable and executable.

Sam Brothwell, Vice President
Sam is Vice President of Strategic and Financial Advisory. Sam’s background includes a decade in utility industry corporate planning and investor relations, fifteen years on Wall Street as a senior equity and credit financial analyst and nearly a decade as a utility and pipeline investor. His background includes electricity, natural gas, and renewable energy. Sam has worked extensively with federal and state policy makers as well as non-government organizations involved in the energy and utility sectors, and he has spoken at numerous industry conferences and investment forums.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
GRE Transmission Incentive Order (Hot Topic)
More Transmission Incentives for Public Power and Cooperatives on the Horizon.
Read the Transmission Hot Topic
Is your EV strategy ready – yet?
Electric vehicles (EV) used to be something utilities thought of as on the horizon, but today they are very much here. The potential for significant increases in electricity sales is obvious, but EV also bring opportunities for enhanced customer engagement and experience. However, there are also considerable challenges related to infrastructure requirements to serve new EV loads, and how to manage or optimize the loads. Retail rates for charging, leasing chargers, charging subscriptions and customer-facing incentive programs function hand-in-hand to harness the opportunities and address the challenges.
MCR is providing a three-part series on EV for utilities, starting with conceptual and strategic issues, to be followed by a tariff-oriented paper and a client case study early in 2023.
Download the “Is your EV strategy ready – yet?” paper
Is your EV strategy ready – yet?
Electric vehicles (EV) used to be something utilities thought of as on the horizon, but today they are very much here. The potential for significant increases in electricity sales is obvious, but EV also bring opportunities for enhanced customer engagement and experience. However, there are also considerable challenges related to infrastructure requirements to serve new EV loads, and how to manage or optimize the loads. Retail rates for charging, leasing chargers, charging subscriptions and customer-facing incentive programs function hand-in-hand to harness the opportunities and address the challenges.
MCR is providing a three-part series on EV for utilities, starting with conceptual and strategic issues, to be followed by a tariff-oriented paper and a client case study early in 2023.
Download the “Is your EV strategy ready – yet?” paper
FRST® Software Demo
Transmission Inflation (white paper)
From 2018 through 2021, the average zonal network transmission rates (Schedule 9) within MISO rose by a compound annual growth rate (“CAGR”) of 9.6% per year compared to an average increase in the Consumer Price Index (“CPI”) of only 2.9% over that timeframe. Much of that increase occurred in 2021 when the MISO systemwide average zonal network rate rose by a stunning 17.7%1to $4.07 per kW/month compared to a CPI of 6.4%. In 2022, the MISO system average network rate rose by 5.2%2to $4.22 per kW/month whereas the CPI is currently running at 8.6% with core inflation at 6%,3levels not seen in four decades. The increases in MISO transmission rates over the years are from consistently high levels of transmission capital spending driven by numerous factors such as wind and solar development, NERC requirements, aging transmission facilities, and retirement of dispatchable power plants. As one transmission owner (“TO”) said, “every time you turn around, there is another reason to invest in transmission.” Now, there is another factor that can significantly raise transmission rates: inflation.
Read the details in our paper.
Upgrading Duquesne Light Company’s low income energy efficiency program tracking system
“MCR’s upgrade to the low income EE tracking system was delivered on time and on budget to significantly improve our staff and implementer efficiency, enhance our reporting capabilities, and modernize our cross-platform data exchanges.”
—Dave Defide, Senior Manager of Customer Programs
Background
Duquesne Light Company built its original low income energy efficiency (EE) tracking system decades ago in response to mandates for a Low Income Usage Reduction Program (LIURP) or “Universal Services” programs. Although the low income EE program was but one initiative in a portfolio of Universal Services programs to support income-eligible customers, the system was built primarily to track the low income EE program. Over time, changes to low income program mandates, designs, and delivery mechanisms caused the purpose-built system to no longer align optimally with the low income EE program compliance requirements, internal management needs, or the implementation process in the field. Furthermore, evolutions in information technology (IT), in particular database systems and interfaces between the low income EE tracking system and the core customer information system, left the current system approaching obsolescence and facing the end-date for underlying software and system support.
Solution
MCR applied our well-defined, structured approach to EE system planning to design a new system; then our utility-specific system development team developed the new system. Deploying the upgraded system without disrupting current implementation contractor scopes of work required replicating those parts of the existing system’s functionality that were still relevant, while bringing the look, feel, and self-service maintenance capabilities of modern systems to bear. A deep dive into compliance and other reporting and management analytic needs allowed the new system to align tightly with them, and to be capable of expansion to track and report one or more of the other Universal Services programs since their compliance, reporting, and internal management analytics needs are similar to those for the low income EE program.
Results
The system was completed in time for Duquesne Light to use it to support of the start of a new EE program year. Duquesne’s third-party implementation contractors were able to easily transition to the new system because it was designed to fit their processes and was similar to the systems they had been using. Duquesne management and staff now have a state of the art system featuring application programming interfaces to supporting systems and a variety of self-service maintenance capabilities. In addition, the system tightly aligns with program compliance requirements and fulfills Duquesne’s reporting needs, including those for management, analytical reporting, and evaluation, measurement, and verification (EM&V) purposes. Going forward, Duquesne will be able to easily expand the system to support additional Universal Services programs.
Upgrading Duquesne Light Company’s energy efficiency program tracking system
“MCR’s upgrade to the EE tracking system was delivered on time and on budget to significantly improve our staff and implementer efficiency, enhance our reporting capabilities, and modernize our web application infrastructure.”
—Dave Defide, Senior Manager of Customer Programs
Background
With the launch of a portfolio of demand-side management programs in response to the passage of Pennsylvania Act 129 of 2008, Duquesne Light Company built an energy efficiency (EE) tracking system to manage its portfolio of projects. More than a decade later, the original system continued to function as designed, but was increasingly difficult to maintain and inadequate for Duquesne’s evolving portfolio of programs. Changes in front- and back-end technologies and the pending retirement of legacy servers necessitated a system overhaul, but internal information technology (IT) resources were fully subscribed with other projects. Additionally, changes in program delivery shifted more activity from traditional downstream programs to mid- and upstream programs. This required better tracking of “bulk” measure data as it came to represent a larger and larger portion of program activity.
Solution
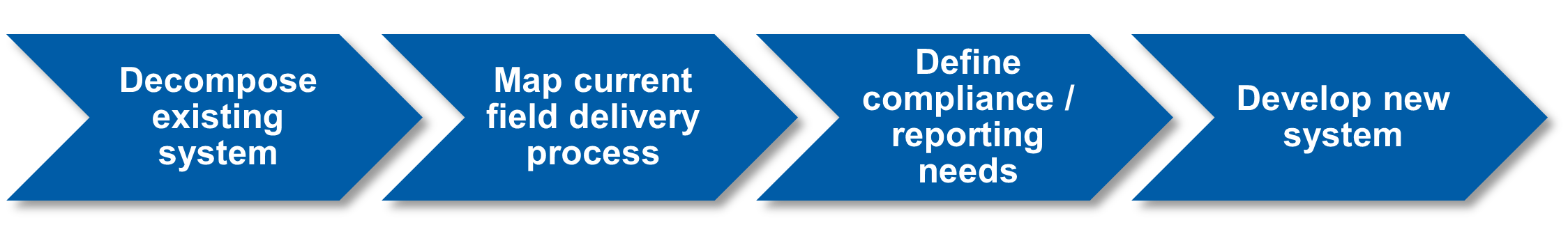
MCR applied our well-defined, structured approach (shown below) to EE tracking system design to understand the current system, specify a new system, then develop that new system using our utility-specific software development team. Throughout this process, the functional and technical teams worked closely together to ensure the needs and design considerations of both groups were incorporated into the project.
To deploy the new system without disrupting Duquesne’s statutorily required program delivery, MCR utilized a phased development and deployment approach that allowed the new system to launch on day one of a new multi-year program phase. This approach required developing an interim customer information retrieval mechanism but allowed the system to launch on time while Duquesne IT continued to work on a more sophisticated customer information application programming interface (API) service. After additional work alongside Duquesne’s IT team, a fully integrated system was deployed in a manner that was completely transparent to the end users.
Results
Duquesne Light went live with the new system on day one of Phase IV of PA’s Act 129 programs and now has a modern, cloud-hosted web application built in Angular and Microsoft SQL Server. Program implementation contractors quickly realized the benefits of additional mechanisms for bulk loading project data. Program management has also benefited from the new calculation engine and increased reporting and data export capabilities of the new system. These capabilities have increased automated compliance with calculation protocols and both the speed and accuracy of responses to internal data requests and regulatory reporting requirements.
Conducting a nationwide market scan to help a small gas utility chart a course for development of its first EE plan
Background
A small Mid-Atlantic gas utility had never run formal energy efficiency (EE) programs when legislation in one of its states required the utility to develop an EE plan, vet it through various stakeholder processes, and file it with the regulator. Being small and lacking EE experience, the client knew it did not want to start from scratch but also did not have sufficient knowledge of what gas EE programs were in the market already or what products and services these programs provided. The client called on MCR to help it build knowledge, understand its programmatic options, and chart a course toward potential development and filing of its first EE plan.
Solution
Given the client’s size, situation, and available budget, rather than lead the client down the usual path of undertaking an EE potential study and a program design process, MCR undertook a broad market scan to identify nationwide measures, incentive structures and levels, and program designs, which resulted in discovering 37 gas measures currently in the field. Program delivery structures included downstream, upstream, midstream, and direct install. A sample of these measures is in the table below:
| Gas EE Measures | |
|---|---|
| Furnace and boiler sizing, equipment and tune-ups | Water restriction devices |
| Per unit (therm, ccf, etc.) custom or performance-based incentives | Various heating and water heating system controls |
| Gas heating and water conversion | Programmable/WiFi thermostats |
| Gas-fired absorption heat pump | Commercial kitchen equipment |
| Infrared heating systems | Water heating systems |
| Various insulation and weatherization measures | Windows |
Results
MCR provided our client a clear understanding of the measure and program options currently being offered in the market. This, in turn, led the client to begin assessing what measures would be most beneficial and market-accepted by its customer base and what incentive levels and program types would best fit its budget. Once a direction is established, the client looks forward to engaging the state’s EE planning advisory stakeholder body with credibility and significant knowledge.
Achieving optimized funding through a value-based decision-making process
“The MCR team has been involved in building our value scoring acumen and helping us to standardize how we score projects across the fleet. Consequently, our engineers in nuclear score projects consistently and can explain variances to those scores.”
—Project Manager
Background
The nuclear division of a large southern utility was challenged with transitioning from subjective risk assessment to a value-based process for evaluating capital projects. The value-based process is supported with an industry-leading asset investment planning and management (AIPM) software solution, already implemented by other corporate divisions.
Every year, the corporate divisions competed for capital funding from an enterprise competition fund. However, this upcoming competition fund was to be awarded through the value-based framework under the new AIPM system. Our client had not implemented the system and was at a severe disadvantage in competing for nuclear project funding; they contacted MCR for help.
Solution
The MCR Nuclear Generation practice worked with our client’s business planning teams at both the corporate and site levels to rapidly implement the AIPM solution. We provided overall project management for the implementation, process mapped the current and future states and updated relevant long range planning processes and procedures. The MCR team configured the AIPM solution specific to nuclear industry needs and developed business cases for capital projects using the new value-based framework to compete for dollars from the enterprise competition fund.
Results
The project resulted in a successful implementation of the AIPM software, allowing for improved data-driven, value-based decisions in developing the overall project portfolio. In the first year of using the new software for the funding competition, the nuclear division successfully demonstrated the value of their projects which resulted in being awarded an additional $27M for their project portfolio from the competition fund.

Ian MacDougall, Consultant
Ian is a Consultant at MCR. He has over 15 years of experience in rates and regulatory affairs, energy efficiency, and revenue decoupling. His MCR experience includes the development of cost of service, revenue allocation, lead/lag studies, rate design, gas and electric energy efficiency programs, and testimony development. He also has prior experience at multiple gas and electric utilities managing and implementing rate design pilot programs, cost recovery mechanisms, revenue decoupling and unbundling procedures, and interrogatory response development.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
The New Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (white paper)
Transmission investment has been consistently strong across the country for many years. Despite high levels of transmission investment, the $1.2 trillion Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (“Infrastructure Act”) includes funding and programs designed to crank up grid transmission and distribution investment even higher, particularly when it comes to promoting interregional and interstate transmission. MISO and SPP could see incremental average annual transmission investment of approximately $410 million and $270 million, respectively. It is unclear whether all this spending will be truly incremental as some of the Act’s funding could end up being used for projects not yet designed but would have happened anyway, given the profitable nature of transmission investment. Nonetheless, if a small public power or cooperative utility happens to be the recipient of a grant or loan that prompts additional transmission investment, the impact could be a significant (albeit temporary) bump up in investment for that particular transmission owner.
Read the details in our Infrastructure Act paper.
MISO Transmission Rates in Joint Zones; Will the Transmission Rate Express Train Continue? (white paper)
MISO transmission rates have been rapidly escalating only to slow in recent years as transmission investment growth has moderated, the number of new transmission owners slowed, and the impacts of the corporate tax cut have played out. In 2021, however, MISO average transmission zonal rates increased by a stunning 17.7%, largely due to a 7.2% increase in transmission investment, a 4.1% decrease in load and the ending of deferred tax refunds. Looking to the next five years, MCR forecasts that zonal rates in joint pricing zones will increase by an average of 6.5% per year, well above the projected five-year inflation rate of 3.17%. We forecast that nine of the 20 joint pricing zones in MISO will see average annual rate increases over the next five years of at least 7%. These forecasted rate increases result from an expanding rationale for transmission investment as “resiliency” combines with social, political and regulatory changes; increasing capital, O&M and A&G costs due to rising inflation; and a continued hunger for earnings growth by IOUs and Transcos. The only way public power and cooperatives can protect their members and customers from the MISO “express train” of rising transmission rates is to develop a business plan to ramp up recoverable transmission investment that increases reliability, ensure no revenue is being left on the table by optimizing the transmission formula rate, and provide other transmission investing benefits to members and customers that make the impact of rising transmission rates more palatable.
Download the MISO Transmission Rates white paper.
Developing an energy efficiency KPI reporting process
Background
While managing day-to-day operations of a comprehensive portfolio of programs and preparing for a new filing with the Commission, the Energy Efficiency Manager of a Mid-Atlantic utility was tasked with reporting portfolio performance key performance indicators (KPIs) to senior management on a monthly basis. Some of these KPIs were straightforward and readily available in the existing energy efficiency (EE) tracking system. Others, however, were not explicitly tracked and required an analytic process to be developed to support monthly reporting. The most challenging of these KPIs was “participation,” as most tracking systems are built around EE measures, not on unique instances of participation. Based on MCR’s track record of successful engagements with the client over more than a decade, the Energy Efficiency Manager asked MCR for help.
Solution
MCR utilized our deep knowledge of our utility client’s data and systems to determine which KPIs could be derived analytically and if there were gaps in the existing data. Working with the client’s implementation contractors, MCR developed a monthly process of collecting additional data to fill those gaps. This process entailed automated email reminders and a web-based data collection form, which ensured consistent and validated data delivery.
Additionally, we established a set of analytic procedures to summarize the KPIs already in the tracking system and to calculate those derived synthetically. In order to improve efficiency and to ensure consistent results for these monthly reports, MCR developed this analytic process with the R programming language.1 Once the data has been collected from the implementation contractors and the EE tracking system, the analysis script need only be run for the full set of KPIs to be computed.
Results
By using our extensive knowledge of the industry, the client’s data system, and modern analytical tools, MCR was able to deliver accurate, monthly KPI metrics covering a number of reporting dimensions, including many that were not directly tracked by program management. The initial KPI report was developed and presented under a short deadline imposed by our client’s senior management in the context of many competing priorities. In addition, MCR was able to ensure consistent reports each month providing our client with high confidence in the results.
_______________
1 R Core Team (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Helping an energy efficiency program continue successfully during COVID
“Our partnership with MCR over the past decade has been exceptional and the success of this program during a very difficult time speaks to the high quality and innovative nature of what could have been a very rough year.”
—Senior Manager of Customer Programs
Background
A mid-Atlantic utility selected MCR Performance Solutions, LLC (MCR) by competitive solicitation to implement a Public Agency Partnership Program (PAPP) and a Community Energy Efficiency Education Program (CEEP). The performance period started in 2016 and ended in 2021. MCR implemented both programs by providing program marketing, participant enrollment, program materials, project development and engineering services as well as facilitating project meetings, training, and logistical support.
In March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted business leading to full or partial closure of educational and governmental institutions across the utility’s service territory. MCR’s implementation of the PAPP and CEEP programs was also interrupted. At that time, on-the-ground PAPP implementers observed unoccupied buildings with onsite operational and maintenance staff who suddenly had a much lighter workload due to workers/students not being able to use the premises.
Solution
MCR proposed, and the utility authorized, a PAPP Directed Self-Install program to retrofit these unoccupied buildings by providing energy efficient lighting at no cost, if participating customers agreed to install the products within 30 days. Key to the initiative, MCR negotiated the bulk purchase of Design Lights Consortium approved fluorescent lamp replacement LEDs with unit cost at or near the original rebate program unit incentive amount. As we began to implement the program, MCR observed a high interest in the supply chain suppliers to provide the LED lighting products. We also experienced a high degree of interest in the program by the utility’s customers.
Results
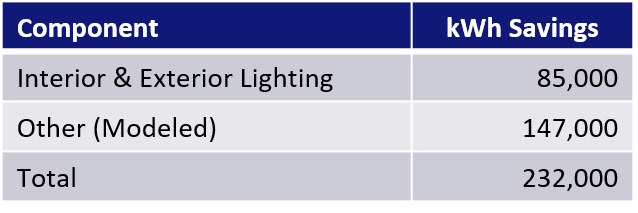
Program launch was instantaneous and PAPP transitioned from an implementation fractured by a global pandemic to recording one of its strongest years in recent history. Over the 13 months of this program, MCR helped place over 220,000 4-foot LED lamps at over 100 customer sites. For the “CV-19 Lamps,” MCR reported almost 8,000 MWh savings, independently verified (to-date) at 130% with a Total Resource Cost (TRC) test cost-benefit ratio greater than 4.0:1.
Life After Lighting: How Utilities Should Retool Their Energy Efficiency Portfolios (white paper)
Recently, there has been federal activity at the Department of Energy (“DOE”) regarding general service lighting (“GSL”), the Energy Independence and Security Act (“EISA”) efficiency standard, and the 45 lumen per watt backstop for GSL. This activity creates for a timely opportunity for MCR to revisit standards, lighting, and “Life After Lighting” for utilities and their EE programs. In a new, short paper we share:
- What actions DOE has taken recently
- The situation with respect to lighting within utility EE portfolios
- A brief review baselines and standards, using lighting as an example
- Recommendations and MCR’s framework for acting on them
Download the paper on life after lighting
Developing a transmission formula rate and protocols for a transmission developer (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
Background
A transmission developer participated in a public policy-based solicitation process and was awarded a segment of a very large transmission line project. The project represented the developer’s entrance into the RTO, which required a new formula rate and protocols. The transmission developer engaged MCR to develop and support the formula rate and protocols at FERC.
Solution
MCR reviewed documents from the project approval process and participated in discussions with the client team to understand the cost elements and terms for the recovery of the project’s costs. The formula rate was then designed and developed to ensure recovery of all allowed costs and the proper calculation of each rate component, including the inclusion of return on equity incentives granted to the client. MCR worked with the client and outside counsel to develop and finalize the associated transmission owner protocols.
Results
MCR’s expertise and management of the formula rate’s development ensured that the cross-functional client team members were in alignment with the calculation of costs included in the formula rate. The formula rate was tested to successfully recover all approved costs and the protocols were approved by outside counsel. MCR’s testimony in support of the formula rate and protocols went unchallenged throughout the FERC Section 205 filing; and the client gained approval for the formula rate.
Helping a large gas utility implement COST™ to allow in-house development of cost of service and rate design
Background
A large gas utility serving over 750,000 customers wanted to purchase a study to run scenarios in house. They also had a desire to be able to run scenarios in two other jurisdictions for rate cases.
The utility engaged MCR to develop the Cost of Service Tool (COST™) to enable the utility to run these scenarios in-house. Ultimately the client wanted to run the model in future proceedings for their rate proceedings and special studies.
Solution
MCR developed their COST™ model using the client’s revenue requirements as an input and created the study as well as integration into the rate design. MCR also provided expert testimony for the rate case regarding the COST™ model and associated rate design. Hands-on training and documentation were provided to the company for their use in the future.
Results
The COST™ model took direct feed from the financial records and revenue requirements model to create an in-house model that was used in a current rate case. At the client’s direction, the COST™ model has the capability to be used in future rate cases in the same jurisdiction as well as two other jurisdictions in which they provide service. Having an in-house model allows the client to continue to use and customize it, freeing them of using consultants on a long-term basis.
Helping a water conglomerate utilize COST™ to achieve budget forecasts in multiple territories
Background
A large water company needed a Cost of Service model to provide full details over 20 jurisdictions and to easily expand when additional properties were acquired.
The conglomerate’s individual territories and acquired companies each had unique models that could not be directly compared to each other. Analysts had to spend valuable time learning each model in order to cross-train with the other areas.
The utility engaged MCR to provide a solution allowing for a single model to be used throughout the company’s 20+ jurisdictions.
Solution
To implement the Cost of Service Tool (COST™), MCR developed a revenue requirements model, complete with standard filing schedules for water and wastewater that could be adapted, as needed, to each jurisdiction’s specific requirements while maintaining a single model’s programming.
The model’s revenue requirement feature also allowed the company to develop a forecast for a 2-year budget throughout its territories.
Results
The COST™ model’s easily adaptable formulas and layout allowed the company to have a singular model for various territories.
Helping an investor-owned electric utility implement COST™ to achieve greater cost transparency
Background
An investor-owned utility was involved in a complex rate case involving significant shifts in rate structure across all classes. The initial Cost of Service filing was prepared using a database tool that provided output without the underlying logic.
Intervenors and commission staff expressed frustration with their lack of access to the underlying logic of the model. The issue became more pronounced as the potential outcomes of the rate case included new rate schedules and a unique proposal to address net metering issues.
The resulting rate order included a provision for the company to adopt a more transparent Cost of Service model.
The utility engaged MCR to provide a solution allowing for robust, error-free modeling of the Cost of Service while providing third parties the access they were promised via the rate order.
Solution
To implement the Cost of Service Tool (COST™), MCR made use of its proprietary mapping tool, which meant minimal changes to the client’s existing datasets. MCR was then able to quickly roll-out COST™, providing an accurate Cost of Service model with the flexibility needed for unknowns of the future.
The built-in scenario capability met third party needs to test alternative allocations and adjustments while ensuring an accurate result. MCR provided the client a separate tool enabling comparison of multiple alternatives.
Results
COST™ supported the utility for its most recent rate case. The flexible architecture allowed for a series of last-minute changes required by the process and ensured a timely submittal.
Cost of Service Tool (brochure)
The Cost of Service Tool (COST™) is the newest addition to MCR’s suite of spreadsheet applications. COST™ is ideal for regulatory professionals seeking to provide greater transparency to regulators, intervenors and other stakeholders. The modeling tool also provides flexibility for in-house scenario analysis and rate design options. Built in Microsoft Excel, COST™ is a fully functional cost of service model with open logic for audit, review and user editing.
Download our COST™ brochure to learn more about the product that adds value to our clients.
Download our IT support requirements for COST™.
Cost of Service Options
MCR works with our clients to determine the best approach to cost of service. We offer a few options for rolling out our Cost of Service Tool (COST™), including licensing the model along with additional consulting support. Download our brief overview, Cost of Service Options for Utilities, to learn more about these alternatives.
Conducting a review of a transmission formula rate (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
“The improved cost recovery from the Attachment O Review is a windfall
for us … the return on investment was immediate and substantial.”—GM, municipal utility
Background
The general manager of a MISO transmission-owning municipal electric utility saw an MCR conference presentation and became interested in MCR’s Attachment O formula rate services. The general manager engaged MCR to make sure the utility was properly recording its costs and optimizing its transmission revenue in its existing transmission formula rate.
Solution
MCR conducted a review of the municipal’s Attachment O formula rate costs, associated work papers and its detailed general ledger accounts. MCR supplemented the review of costs with interviews of key operating and financial personnel to understand their day-to-day activities. These two steps ensured the client was recording its distribution and transmission assets and expenses consistent with the FERC Uniform System of Accounts and the MISO tariff. Along the way and also in a workshop setting, MCR provided education regarding the proper recording of costs and the optimization of allocators used in the Attachment O.
Results
The Attachment O Review resulted in improvements to how certain costs were recorded and led to modified timekeeping processes to ensure costs were recorded consistent with FERC accounting. The client achieved a substantial increase in annual transmission revenue by placing its existing transmission-related expenses in the proper categories and ensuring field personnel were charging the proper accounts, with a particular emphasis on the appropriate recording of transmission vs. distribution wages. The additional annual revenue eased budget concerns, helping the client to fund additional necessary capital projects. The Attachment O Review also resulted in a more educated and confident staff that now has an in-depth understanding of Attachment O related assets and expenses and how allocators impact revenue, providing staff with the ability to make more informed business decisions going forward.
Utility Financial Modeling: Spreadsheets Can Deliver Results (point of view)
Financial and regulatory analysts working at utilities understand the need for utility-specific models as the unique challenges of utility forecasting cannot be shoehorned into a model built for other types of businesses. No other industry requires the type of logic needed to translate forecasts of expense, revenue and capital investment into an integrated whole while providing insight into the business. Whether its earnings forecasts for investor-owned utilities or financial metric analysis and rate forecasts for public and cooperative entities, forecast groups must provide models that generate reliable and defensible answers. Modeling for utilities is complex, leading some analysts to believe that the complexity does not lend itself to spreadsheet modeling. But advances in technology and modeling practices make spreadsheets a superior choice for both accuracy and flexibility.
Download the MCR Point of View.
The Four Reasons Why Battery Storage Will Gain Traction in MISO and SPP (white paper)
In 2021, front of the meter utility-scale battery storage will continue to grow rapidly in certain states and will begin to make a significant difference in some wholesale markets, most notably the California ISO (“CAISO”). By contrast, even though the interconnection queues for storage have been increasing in size in MISO and SPP, the practical impacts of battery storage are not likely to be reflected in these wholesale markets for the next few years. By 2025, however, MISO and SPP will join CAISO in experiencing widespread adoption of storage. Once growth starts accelerating in MISO and SPP, it will be very difficult to keep up and meet both the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead if utilities are not prepared.
Download the Battery Storage white paper.
MCR Transmission Strategy Services (brochure)
MCR helps G&T cooperatives, municipals, public power districts and joint action agencies in SPP and MISO realize the full revenue potential from their transmission assets. We use a collaborative approach for all our transmission engagements with the goal of finding and generating value for our clients. Download our brochure to learn more about the services that add value to our clients.
Download the MCR Transmission Services Brochure
Achieving Significant O&M Reduction with Risk Informed Budgeting (white paper)
The utility industry is undergoing dramatic change as new technologies, such as solar and batteries, threaten to disrupt the traditional utility generation model and may have a dramatic impact on revenues. At the same time, costs are increasing as interest rates rise, distribution systems are reworked to adopt two-way flow of power, and customer expectations drive the need to support new channels for information and transactions. Combined, these trends are placing significant pressure on earnings.
To address these pressures, utilities frequently look to traditional cost cutting methods to meet financial performance objectives: flat percentage or across-the-board cuts in base budgets, staff reduction or deferred project spending. While these traditional methods may achieve some results, a more analytical approach to optimize spending will help ensure the right funding is applied to the right efforts at the right time.
Risk Informed Budgeting is an analytical approach to budgeting where the timing, amount and consequence of every budget line item is challenged. In our experience, an effectively implemented Risk Informed Budgeting program can produce 10% to 15% savings in routine budgets, even after implementing other cost reduction initiatives.
Read the Risk Informed Budgeting white paper
Helping a generation business unit optimize preventive maintenance projects during an outage
Background
A generation business unit was planning the maintenance outage scope for its nuclear plant and had an extensive list of Preventive Maintenance projects as candidates for inclusion in the outage plan. Given the high cost of having the plant offline for maintenance work, the generation business unit was considering Preventive Maintenance Optimization (PMO) to optimize the number of Preventive Maintenance projects (PM) undertaken at its nuclear plant during the outage. Knowing that many PMO efforts are challenging to perform, lack the bases to change PM labor burdens and may even create more PM work orders, the generation business unit reached out to MCR for help.
Solution
MCR used our proprietary categorization approach based on management’s ability to influence the scope and/or schedule of each PM. Our categorization approach incorporated documented requirements, evidence of asset performance plus consideration of risk attributed to scope and schedule determinations.
All PMs were reviewed as if no frequency currently existed, establishing a recommended frequency for the very first time. PMs were grouped according to the plant equipment hierarchy where possible with operational consideration given to every PM. MCR then made recommendations based on our risk-informed methodology where consideration was given to the probability of an adverse consequence as an outcome of establishing PM scope and periodicity. All information was presented and reviewed in workshops with Engineering asset owners to identify any special circumstances for any PM.
Results
The project produced a matrix of all PMs in outage scope with current PM information and other valuable data including:
- Categorization of each PM based on management’s ability to influence scope or schedule
- Potential consequence related to reducing the PM burden
- Probability of the consequence occurring
- Information sources and references supporting recommendations
- Measure of Engineering support for each recommendation
The project discovered information necessary to establish proper PM scope and schedule and fostered ownership of PM recommendations by the individual asset owners. The combination of improved labor estimates reducing overall labor cost plus condition-based adjustments of PM next due dates identified potential savings of more than $2M for a single maintenance/refueling outage.
The Age of Alternative Ratemaking (paper)
The use of Alternative Ratemaking Mechanisms (“ARM”) is not a new concept. Yet, despite its solid record of being beneficial to utilities, regulators, and stakeholders, it has historically had a slow level of adoption by many states. That has now changed, and we are entering a new regulatory age: The Age of ARM. Even states that have been extremely reticent to shift away from the traditional rate design methodology are now moving to embrace the use of alternative ratemaking. Whether or not your state has adopted the use of ARM, it is important to consider ways in which these mechanisms could create both opportunities and challenges.
Environmental Advocates Have Proposed a Sweeping New Approach to Regulating Utility Capital Investments and Earnings (News Alert)
On August 19, 2020, the organization E4TheFuture, whose mission is to “promote residential clean energy and sustainable resource solutions to advance climate protection and economic fairness by influencing… policies,” released a new publication titled, “National Standard Practice Manual for Benefit-Cost Analysis of Distributed Energy Resources” (“NPSM for DER”). Under the direction of E4TheFuture, advocacy-oriented firms such as Synapse Energy Economics and Energy Futures Group, as well as the agenda-driven Smart Electric Power Alliance, authored this manual. E4TheFuture is working with regulatory commissions and other stakeholders to encourage adoption of the ideas presented in the NSPM for DER; if embraced by policy and regulatory actions, the NSPM for DER will dramatically affect how electric and gas utilities plan, make investments and create earnings.
MCR’s Cost and Rate Competitiveness Services (brochure)
Click here to download the Cost and Rate Competitiveness Services brochure
MCR provides transmission strategy support to municipals, public power districts, joint action agencies, G&Ts, T&D cooperatives, and independent transmission developers in various RTOs. Our clients have a goal of optimizing the value of their current and future investments in electric transmission. We help them understand their costs and realize the full revenue potential from these transmission assets. MCR’s Transmission Strategy practice provides the following services:
Transmission Cost/Rate Competitiveness (see earlier pages for more detail)
- Peer Cost Comparison by FERC Account
- Rate Strategy and Transmission Revenue Forecasting
- Transmission Capital Investment and Metric Comparisons
Transmission Formula Rate Analysis
- Formula Rate Review for Existing Transmission Owners
- Development of ATRR for New Transmission Owners
- Review/Challenge to Incumbent IOU Formula Rate Costs
- Staff Education Workshops on Transmission Formula Rates
FERC Filings
- Section 205 Rate Filings – Testimony and Formula Rate Support
- Transmission Incentive Rate Filings and Testimony
- Cost of Capital Expert Testimony
- Intervention and Settlement Support
Strategic Economic Analysis
- Analysis of Joint Zone Investment and FERC 7-Factor Test
- Analysis of Potential Purchase or Sale of Transmission Assets
- Economic Evaluation of New Transmission Projects
- RTO Membership Evaluation
- Development of Transmission Business Plans
The Seven Potential Threats to the Transmission Business: Is Transmission in SPP Still a Solid Business? (white paper)
Over the past decade, the transmission business has been lucrative for most transmission owners in SPP transmission. Transmission investment has been a driver of earnings growth for investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) and transmission companies (“Transcos”), while providing high returns for public power and cooperatives. On the horizon, however, there are numerous potential threats to the transmission business and to transmission owners’ ability to sustain high levels of new investment. MCR believes that although some of these threats may eventually have an increasing impact on future investment opportunities, there are factors that mitigate these threats. Transmission will continue to be a strong business in SPP through at least the mid-2020s.
Download the Threats to Transmission Business white paper.
Helping Duquesne Light Company design and implement energy efficiency programs to meet its Pennsylvania Act 129 obligations over three multi-year phases
Background
Signed into law by Governor Ed Rendell in 2008, Pennsylvania Act 129 required Duquesne Light Company, and other electric distribution companies in Pennsylvania, to develop cost effective plans that would reduce electricity consumption across their service territory by one percent by 2011 and three percent by 2013. In order to meet these requirements and as a result of a competitive bid process, Duquesne Light selected MCR to design and implement an energy efficiency and demand response plan.
Solution
MCR worked with Duquesne Light to develop an energy efficiency potential forecast and create a portfolio of 17 energy efficiency and demand-response programs serving the residential, low income, commercial, industrial and governmental customer sectors. The programs were designed and benchmarked to best practices to achieve savings in the market segments identified by the potential forecast.
Working with the regulatory and legal teams, we developed the filing and expert testimony for the Phase I plan and participated in interactions with the Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission (PUC or Commission). After the Commission approved the plan, we helped the client’s energy efficiency department develop operational processes and supporting systems; assisted with the solicitation, evaluation and selection of program implementation contractors; and interacted with the statewide evaluator and EM&V consultant to address evaluation, measurement and verification matters.
Results
Duquesne Light achieved energy efficiency savings at 123% of the Phase I goal. Portfolio EM&V realization rates exceeded 95% as measured by an independent evaluation contractor and confirmed by the Pennsylvania PUC Statewide Evaluator. Following achievement of this milestone in 2013, MCR continued to work with Duquesne Light to achieve its Phase II (2013-2016) plan goal and Phase III (2016-2021) plan goal.
In addition to helping Duquesne Light achieve its energy savings goals, MCR has helped our client design, develop and implement leading-edge programs for its customers, including:
- Public Agency Partnership program
- Schools Energy Pledge program
- Community Education program
- Low income multi-family passive house program
- Commercial “self-install” LED lighting program
These programs and others have established our client as an innovator in energy efficiency in Pennsylvania.
Helping a multi-district water utility calculate revenue requirements through implementation of an integrated regulatory analysis system
Background
A water utility with multiple districts wanted a tool to calculate revenue requirements and develop the standard filing requirement reports for one of their states. The tool needed to calculate all districts concurrently, be easy to maintain and be highly accurate. The team also wanted to bring cost of service modeling in-house rather than continue with a consultant. The utility turned to MCR to address their problem.
Solution
MCR developed an integrated system that combined revenue requirement modeling and cost of service modeling with MCR’s Cost of Service Tool (COST™). Key features included an easy-to-use mapping tool to capture new GL accounts from test year data, automated loading of data to ensure model reliability and a fully functional print control panel to easily generate needed outputs for filing. The model was customized to provide the required filing documents for the utility’s state regulatory commission. The model provided a data feed to the cost of service logic to calculate cost of service by rate schedule and utility district.
Results
MCR’s COST™ model was implemented prior to a rate case and completed in 8 weeks. Client staff were able to substantially reduce filing development time and improve their ability to adopt last minute changes as part of their settlement process. The model has since been expanded to provide a two-year revenue requirements forecast to enable planning for future rate cases.
Helping a multi-district water utility calculate revenue requirements through implementation of an integrated regulatory analysis system
Background
A water utility with multiple districts wanted a tool to calculate revenue requirements and develop the standard filing requirement reports for one of their states. The tool needed to calculate all districts concurrently, be easy to maintain and be highly accurate. The team also wanted to bring cost of service modeling in-house rather than continue with a consultant. The utility turned to MCR to address their problem.
Solution
MCR developed an integrated system that combined revenue requirement modeling and cost of service modeling with MCR’s Cost of Service Tool (COST™). Key features included an easy-to-use mapping tool to capture new GL accounts from test year data, automated loading of data to ensure model reliability and a fully functional print control panel to easily generate needed outputs for filing. The model was customized to provide the required filing documents for the utility’s state regulatory commission. The model provided a data feed to the cost of service logic to calculate cost of service by rate schedule and utility district.
Results
MCR’s COST™ model was implemented prior to a rate case and completed in 8 weeks. Client staff were able to substantially reduce filing development time and improve their ability to adopt last minute changes as part of their settlement process. The model has since been expanded to provide a two-year revenue requirements forecast to enable planning for future rate cases.
Helping a vertically integrated utility develop a strategy and roadmap to engaging stakeholders in a new regulatory framework that closely aligned integrated resource planning and energy efficiency
Background
A large, vertically integrated utility found itself challenged by the need to comply with new integrated resource planning (IRP) and energy efficiency (EE) legislation and regulatory commission implementation guidance after contention in the prior IRP filing and process, and amidst criticism of EE efforts by energy and environmental advocates. With multiple parties involved and several issues being conflated, the client turned to MCR for help.
Solution
MCR EE and Regulatory staff worked with the client to define an approach to strategy development and execution that was driven by a daylong workshop including client EE, regulatory, forecasting and resource planning staff. A key objective of the workshop was to identify and align around the issues and begin to develop a stakeholder engagement strategy. The workshop revealed many issues, proceedings, and processes to address:
- IRP law
- EE law
- Regulatory commission guidance
- EE plan
- IRP/Generation certificate of necessity (CON)
- Sustainability plan
There were underlying forecasting, modeling, and planning processes that had become contentious with the regulator, statutory parties, and the energy/environmental/eco-justice intervenors, all of whom were critical of various aspects of the interrelated, but largely siloed utility processes. MCR facilitated a deep dive into the issues via a disciplined process that examined the background, parties, client objectives, client positions and the impact on the client for each of several issues. We developed an overarching strategy built around six strategy statements and extended them to include action items and metrics by which to assess success.
Results
As a result of the engagement, the client achieved a depth of understanding and a level of consistent internal awareness beyond what existed previously. The seeds of deeper internal collaboration, alignment and consistent engagement of external stakeholders positioned the company well for its going-forward work on the issues and within the various proceedings and processes.
Helping a mid-size utility client deeply understand its low-income and government, non-profit and institutional markets
Background
As part of its triennial energy efficiency (EE) planning process, a mid-size utility client wondered how much savings it could capture, and at what cost, by focusing on its low-income and government, non-profit and institutional (GNI) markets. In effect, they wanted a deep dive into market characterization and a forecast of economic potential in seven specific segments that together comprise their low-income (residential) and GNI (commercial) markets. The utility engaged MCR to help them clarify objectives and specific questions, and to develop the characterization and forecast.
Solution
MCR brought a novel approach to the project. Whereas most market characterization and market potential work relies on the federal energy consumption surveys (i.e., the residential and commercial buildings energy consumption surveys, RECS and CBECS in this case) and Census data, MCR instead relied upon primary data from the utility’s own systems and staff. We interviewed 12 staff and worked with database analysts from multiple functional areas to develop a total of seven data queries. As a result of the interviews, we also identified or mined numerous local or service territory-specific secondary data resources. With primary and recommended secondary references in hand, MCR folded in analysis of the RECS, CBECS and Census data to develop basic descriptive statistics of the markets of interest. The outcome was a realistic grasp on the size and basic nature of the identified market segments that became the foundation for our work on three typical elements of market characterization and potential studies.
MCR used the most recent utility sales forecasts and FERC Form 1 data to develop baseline and forecast numbers of customers and loads by high-level customer class, and then decomposed the major customer classes into the identified segments and even more granular sub-segments (e.g., low income single family, low income multifamily, and mobile homes) using a combination of the utility-specific data and federal data as described above. We characterized the segments by applying staff interview insights, queries of the utility’s multiple database systems, and the RECS and CBECS microdata, that is the specific line-by-line survey responses, for 15 building types judged to represent all or most of the building stock in each identified segment. Rather than conduct a ground-up potential study that would require considerable investment of time and money, MCR conducted a meta study of recent potential studies in the client’s states and five neighboring states to develop annual and ten-year percentages of sales that could be cost-effectively saved by EE programs. We were then able to develop base, high, and low potential forecasts for each of the seven identified segments. Finally, we applied the acquisition cost ($/first year kWh saved) by high-level program from the approved EE plan to develop corresponding budgets.
Results
The novelty and granularity of MCR’s approach, and the strength of a potential meta study were well-received by the client and the resulting information continues to provide insight for internal strategy and planning into the amount of EE headroom available in the historically hard to reach low-income and GNI markets, and the cost to achieve such savings.
Building a detailed rate forecast for a G&T with multiple rate classes
Background
A large G&T sought to replace a black-box forecasting model with a tool that could support detailed forecasting of revenue requirements that matched the utility’s cost of service for each of its member classes.
Solution
MCR implemented its Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™) with a client team comprising experts across the finance and planning groups. The model needed to be configured to develop a revenue requirement for each of the G&T’s generating assets as member participation in each asset defined the rate class. FRST™ was configured to enable a dispersed planning process where internal experts developed detailed plans in various models and database tools. Each of these outside models was configured to generate an upload file that can be quickly uploaded into FRST™. The modeler responsible for coordinating the forecast has minimal inputs beyond a handful of miscellaneous entries and key drivers. The model’s ledger is mapped to the latest cost of service, which allows a consistent view of the forecast over time and allows members to see the impact of various strategies on the cooperative as a whole as well as their individual rate.
Results
The FRST™ model was implemented quickly and has continued to prove its value. Recently, the model was used to evaluate the shutdown of various coal resources. This analysis was simplified given the model was configured to provide a forecast of revenue requirements of each individual generating station, thereby easily showing the total revenue requirement with and without the assets. Each member was able to see the direct impact on their distribution cooperative supporting a more informed decision by the board.
Updating FRST™ with new regulatory strategy capabilities
Background
MCR’s client is an IOU that had implemented a version of MCR’s Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™) that focused on short-term earnings forecasting. The initial implementation was based on the Regulatory group providing all aspects of information for future rate cases. The resulting process worked in an environment with few rate cases; but after time, the utility began seeing more frequent rate cases and had a need to better link financial forecasting and regulatory planning.
Solution
MCR worked with the client to incorporate our regulatory planning logic into a refreshed version of FRST™. The new model provided a detailed regulatory panel, so the analyst had greater flexibility to define all needed inputs for determining potential rate changes. These changes included flexible test years, options for building ratebase and adjustments to revenue, expense and ratebase. Through FRST™’s import and mapping modules, the new model uploads data from the Regulatory group on current ratebase and develops the revenue requirement instantaneously.
Results
With FRST™’s flexible architecture, the new regulatory logic was easily incorporated into the model while preserving all the unique functions that were customized for the original model implementation. The analyst now quickly identifies issues related to future rates and works with the Regulatory group on strategies to address them.
Developing a regulatory strategy capability for an IOU
Background
A large utility owned electric, gas, water and wastewater utilities across a multi-state area. As they focused on growth through acquisition, they lacked the ability to analyze each entity’s need for rate cases consistent with their planning horizon.
Solution
MCR configured its Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™) to support annual planning with a seamless integration with the client’s financial system and reporting tools. The model loads data from supporting systems, which include the operating and capital budgets from the multiple utility districts. MCR developed a regulatory control panel, which allows users to adjust key factors, including test year date range, rate effective dates, rates of return, and capitalization ratios. The model also provides flexibility for building up ratebase, allowing the user to include/exclude items and determine the time period (e.g., 13-month average, end of period, etc.). Coupled with the regulatory panel, FRST™’s logic solves for revenue requirements for both historic and future test years without complex macros or circular references. Users are able to test various scenarios and adjustments to revenue, expense, ratebase and any high-level driver. The individual utility districts are on a common platform ensuring consistency across their forecasts.
Results
MCR completed the model and the client is now analyzing potential strategies. Within a year, the model was easily expanded to incorporate a number of newly acquired utilities. Client staff was able to develop the additional components with minimal assistance from MCR. FRST™’s flexible architecture supports continued growth in their business.
MISO’s New Criteria for Market Efficiency Projects (white paper)
On April 30, the Midcontinent Independent System Operator’s (“MISO”) filed proposed revisions to its tariff in an effort to substantially expand the number of Market Efficiency Projects (“MEP”) that would be available for competitive bidding. These revisions were the result of more than four years of stakeholder discussions between MISO and a group of participating MISO Transmission Owners (“TOs”). The compromise reached by this group focused on broadening the benefits included in the economic evaluation of MEPs, lowering the MEP project voltage threshold, and more precisely assigning the costs of MEPs. But despite this lengthy, well intentioned effort, these changes are unlikely to bring the desired, dramatic change envisioned for the transmission market.
Download MISO’s New Criteria for Market Efficiency Projects white paper

Patrick McDermott, Manager
Patrick is a Manager at MCR. He has 9 years of experience in the nuclear energy industry in the areas of reliability engineering, design engineering and probabilistic risk assessment. Patrick uses his expertise to respond to client issues through application of technology, analytics and data-driven solutions. He has played an important role in advancing MCR’s capabilities in driving cost-effective nuclear operations.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
Conducting a transmission formula rate review and education of client staff for a joint action agency (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
“Everyone I know would do well to have MCR come in at least once to do a review. It’s good to have an independent resource that isn’t attached to (the RTO) … for our agency and three of our members, MCR was able to point out some significant areas where we weren’t recovering all we could; and, for one of those organizations, those numbers were substantial.”
—CFO
Background
A joint action agency had been a transmission owner in an RTO for many years. Faced with changing RTO formula rate protocols, the client wanted to ensure that its transmission costs were properly recorded and documented, and its transmission revenue was being optimized within the framework of the RTO tariff.
Solution
MCR conducted a review of the client’s transmission-related cost information to ensure they were recorded in accordance with FERC’s Uniform System of Accounts. MCR also pointed out opportunities to increase transmission revenue within the confines of the formula rate.
During a day-long staff workshop session, MCR educated key company and member personnel on the components and allocators in the formula rate and the new RTO protocols, including the required work papers.
Results
As a result of the review, the client made some adjustments to its recording of costs and work papers, and capitalized on ways to increase transmission revenue. Overall, the client staff developed a deeper understanding of the formula rate details and is now better equipped to answer formula rate questions from stakeholders and the RTO.
Enhancing a distribution cooperative’s financial forecasting capabilities with FRST
“MCR was able to automate feeds of data coming from different supporting parts of the organization. They included rating reports based on their knowledge of recent releases and updates of Moody’s, S&P and Fitch ratings criteria. I use the FRST™ model on a monthly basis to give updates to our executive management and to our Board of Directors.”
—Dede Jones, Chief Financial Officer, IREA
Background
Intermountain Rural Electric Association began implementing a series of projects to improve their internal processes for forecasting, planning and budgeting. A key area of concern was having robust capabilities to develop a financial forecast. The existing financial forecast was conducted once a year on a home-grown spreadsheet that posed significant challenges.
IREA engaged MCR to implement the Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™) to become a primary tool for monthly forecasting and annual planning.
Solution
Key to the success of the project was the development of a solution that seamlessly combined various analyses and forecasts across the organization and leveraged existing tools. A unique challenge for IREA was combining details from their power provider with information on their jointly owned resource. The incoming data from their partner provided information on purchases, sales and all forecasts related to the unit, including capital spending and O&M.
FRST™ took direct feeds from key supporting forecasts, including the budget system, debt datasets, information from power supply and the capital budget. The model was primarily driven by the uploaded data allowing the user to focus on key drivers and analysis rather than cutting and pasting data. Sophisticated error checking helped quickly identify key changes in the model that might affect the outcome of the plan
Results
The new model was implemented in a rapid manner and immediately began to support IREA’s analysis of its current financial situation and to make critical decisions related to the Cooperative’s current strategies.
Developing a transmission formula rate template for a joint action agency (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
“MCR’s forward-looking test year and construction work in progress analysis helped justify our filing with our internal Board, as well as the ultimate filing with FERC, which was subsequently approved.”
—Transmission Planning Manager
Background
A joint action agency decided to invest in two major new transmission projects. The client discussed with MCR the prospect of filing for transmission rate incentives and a forward-looking test year in order to optimize the cash flow benefits from the projects.
Solution
MCR conducted a quantitative analysis that showed there was substantial net present value benefits to the joint action agency from: (1) receiving incentives of a hypothetical capital structure and recovery of construction work in progress in rate base; and (2) changing from a historical-based formula rate to a forward-looking rate. MCR supported the client and its Washington-based legal counsel in its request for incentives.
Additionally, as a result of the incentives and a forward-looking test year, a separate Section 205 FERC filing was completed to implement the changes in the pro forma formula rate template. With regard to the request for a forward-looking test year, MCR developed the filing outline, drafted testimonies (sponsored by the client and MCR) and provided the required changes in the standard template to implement the changes in the pro forma formula rate.
Results
MCR’s client received a favorable ruling, allowing them to move to a forward-looking test year. We continue to work with our client and RTO tariff personnel to ensure a smooth transition to the new forward-looking rate.
Conducting a review of the transmission formula rate of a nearby incumbent IOU (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
“MCR are in-depth experts on the Attachment O… I was flabbergasted MCR was able to gather so much information. They had all the appropriate questions for the IOU.”
—Director of Finance, municipal utility
Background
A municipal utility was faced with rapidly rising transmission rates from the neighboring incumbent IOU transmission owner. It had been many years since the municipal conducted an in-depth review of the IOU’s transmission costs. The municipal engaged MCR to review the IOU’s transmission formula rate template to ensure the costs were accurate.
Solution
MCR conducted an in-depth review of the neighboring IOU’s formula rate and work papers. MCR worked with the client to question the IOU about areas requiring further explanation or areas of concern and assisted the client in understanding some of the more nuanced aspects of the formula rate.
Results
MCR produced a detailed analysis for the client focused on the causes of the transmission revenue increases for both the true-up and the changes in the upcoming year compared to the prior year. MCR also provided a look to the next year’s reporting period, including the potential impact of an ROE reduction and the impact of a change in the IOU’s income tax rate. The client was pleased that it could report to its Board that an in-depth review of the IOU’s costs was conducted, the IOU’s revenue requirement was being accurately calculated and that the municipal did not have to proceed with any formal challenge process or filings with FERC.
MCR Online Demonstrations
MCR is on the forefront of identifying Beneficial Electrification (“BE”) opportunities and analyzing them from the perspectives of key stakeholders in order to assist clients with design and eventual launch of pilots or fully scaled programs and/or products.
Key Stakeholders
Recognizing that various definitions for “Beneficial Electrification” exist, MCR begins with the following working definition and customizes it to frame client efforts to their exact need: “Beneficial Electrification is a means of powering end-uses of energy with electricity; by doing so, the action must include at least two of the following without adversely affecting the others: 1) Does not negatively impact the environmental and reduces GHG emissions/pollutants, 2) Saves consumers money in the long-term, 3) Improves the quality of life for consumers, or 4) Provides enhanced grid management, efficiency, or other benefits.”
MCR provides modeling expertise, regulatory and rate guidance, marketing channel and product delivery expertise, and guidance to balance internal and external stakeholder interests.
Current projects include:
- Development of candidate BE hypotheses, for example how a targeted electrification program can benefit the client and its customers.
- Testing BE hypotheses through detailed technical comparison of end use technologies via our robust BE model.
- Configuration of MCR’s transparent, and flexible BE model to include:
- Retail and avoided costs of electricity, natural gas, propane, heating oil, gasoline, diesel fuel.
- Quantification and monetization of emissions benefits.
- Quantification of operations & maintenance costs for efficient, electrified technologies and baseline technologies, for example when considering heat pump technologies versus incumbent fossil fuel technologies, and internal combustion engine vehicles versus electric vehicles.
- Application of MCR’s BE model for:
- Forecasting technical, economic and program achievable potential.
- Cost effectiveness based on the California Standard Practice tests, utility return on investment (ROI) and customer total cost of ownership (TCO) and/or break-even point.
- Customized program design for the client.
- Regulatory support for the development and defense of client electrification filings seeking approval and cost recovery of proposed program
The Growing Imperative for Natural Gas Energy Efficiency – American Gas Foundation
The American Gas Foundation (AGF) engaged MCR to evaluate the full range of current and future potential benefits that could accrue from natural gas utility energy efficiency (EE) programs, including 1) the current state of gas utility EE cost-effectiveness, and 2) perspective potential future benefits. The report provides an in-depth survey of existing natural gas utility EE programs as well as potential future program approaches and incentive strategies. The study also highlights opportunities to leverage indirect and non-energy benefits stemming from optimal and efficient use of natural gas delivery infrastructure.
Pilots for the Changing World of Energy Efficiency (thought piece)
The challenges, demands, and scope of utility energy efficiency (EE) programming are all rapidly changing, bringing a need for real innovation. All parties designing and approving EE plans have been focused on the problem of how to make up for energy and demand savings no longer available from screw-in LED and other lighting, but there are other factors making innovation an imperative. In this piece, we take a look at how MCR combines regulatory and stakeholder expertise with cross-cutting EE services to ensure innovation continues to be successfully developed and implemented at our utility clients.
Download the MCR thought piece.
Conducting a review of the transmission formula rate of neighboring IOU (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
“MCR went through the cost data with a fine tooth comb and asked the incumbent IOU some very hard questions.”
—Financial Planning Manager, joint action agency
Background
A joint action agency was faced with an unusually large transmission true-up charge and was concerned the neighboring IOU made a significant analytical error. The agency engaged MCR to conduct a review of the IOU’s transmission rate true-up and its projected transmission formula rate for the upcoming year to better understand the causes of the true-up amount, and to ensure the rate calculation was accurate and all of the included costs were appropriate.
Solution
MCR conducted an in-depth review of the IOU’s formula rate and supporting work papers. This analysis included identifying the variances and the drivers of the variances between the forecasted costs and load, and the actual costs and load. MCR worked with the client to develop a series of questions for the IOU about areas requiring further explanation or areas of concern.
Results
MCR produced a detailed analysis for the client reflecting the causes of the transmission rate increases for both the true-up and the forecasted changes in the upcoming year compared to the prior year. In some cases, the IOU made corrections to the revenue requirement or added additional information based on the questions from the review. The client was pleased that it could report to its Board that an in-depth review of the IOU’s costs was conducted and that the true-up amount was correct with some minor adjustments. The client used the report as back-up in case its auditors asked any questions. The client later engaged MCR to review the IOU’s production formula rate and the transmission formula rate in subsequent years.
Conducting a review of a transmission formula rate (Transmission Formula Rate Analysis)
“Engaging MCR is one of the true investments a utility can make that will really pay off… I’ll tell you there’s a lot more utilities that could use this kind of help. The upfront cost is certainly worth the reward.”
—GM, municipal utility
Background
A municipal electric utility, which is an existing transmission-owning utility in MISO, wanted to ensure that its transmission-related costs were being properly recorded in the MISO Attachment O cost template and that they were optimizing their annual transmission revenue requirement (“ATRR”), consistent with the tariff.
Solution
MCR conducted a review of the municipal’s Attachment O formula rate, workpapers, and their detailed general ledger accounts, and conducted interviews with key management and staff. MCR worked with the client to modify and sharpen the set of internal accounts that are now mapped to the FERC Uniform System of Accounts and consistent with the RTO tariff. The revised account structure resulted in a clearer and more defendable separation of generation, transmission and distribution assets and expenses, and identified recoverable costs that were being “left on the table.” MCR also worked to integrate improved timekeeping processes consistent with the new account structure.
Results
The results for this municipal client fall into three areas: 1) cleaner numbers for all functional departments, leading to more effective budgeting with transparent actual spending and more targeted priorities in capital planning, 2) a substantial increase in the recovered transmission ATRR, easing pressures on the municipal’s budget, and 3) a more educated staff that now has an in-depth understanding of Attachment O related assets, expenses, and how allocators impact transmission revenue. More effective budgeting and a more educated staff lead to more informed business decisions going forward.
The Seven Potential Threats to the Transmission Business. Is Transmission in MISO Still a Solid Business? (white paper)
Over the past decade, the transmission business has been lucrative for most transmission owners in MISO. Transmission investment has been a driver of earnings growth for investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) and transmission companies (“Transcos”), while providing high returns for public power and cooperatives. On the horizon, however, there are a number of potential threats to the transmission business and to transmission owners’ ability to sustain high levels of new investment. MCR believes that although some of these threats may eventually have an increasing impact on future investment opportunities, there are factors that mitigate these threats. Transmission will continue to be a strong business in MISO through at least the mid-2020s.
Download the Threats to Transmission Business white paper
Forecasting electric vehicles and photovoltaic systems for Indianapolis Power & Light’s Integrated Resource Plan
“Having a third party complete this analysis was essential to IPL; MCR was knowledgeable, provided a well-done report, and presented the material really well. MCR is very organized and on top of project management. They have great communication. They are very easy to work with.”
—Erik Miller, Senior Research Analyst
Background
While developing its 20-year integrated resource plan, Indianapolis Power & Light Company (“IPL”) needed to incorporate electric vehicles (“EV”) and behind the meter distributed solar photovoltaic technology (“PV”) into its load and sales forecasts. The regulator and stakeholders were interested in seeing the effect of these two electro-technologies on the IPL forecast that would drive development of its preferred resource portfolio. With the goal of developing a reasonable and defensible forecast that could be easily explained, IPL approached MCR for help.
Solution
The MCR team brought deep research and analysis experience with EV and PV technologies, as well as experience with statistical modeling and utility load forecasting. We began the project by gathering background information on EV, PV, rates, and market data, including interval sales (kWh energy) data from IPL, MCR’s data libraries, and online resources, such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (“NREL”) PVWatts system. From this data, we defined prototypical EV and annual charging consumption, as well as residential and commercial PV systems and sizes. We then applied IPL sales data for applicable rates and riders to assemble 8,760-hour (annual) load curves for light duty (i.e., cars, pick-up trucks, etc.) EV charging and, adding PVWatts data for PV production. This analysis established a baseline and drove MCR’s approach to first forecast the annual number of units of EV, residential PV, and commercial PV, and then apply the prototypical system load data to develop the energy and capacity impacts by rate period. The key modeling challenge, therefore, was to develop 20-year forecasts of the number of units of EV and PV.
To resolve this challenge, MCR considered approaches to forecasting numbers of units of emerging technologies (market adoption), often referred to as the Sigmoid Adoption or S-Curve. Such modeling is usually driven by logistic and similar regression techniques and mathematical models, such as the Bass Imitation Model. Forecasting technologies that are early in their market adoption, such as EV and PV, depends on many inputs and assumptions (e.g., pace of innovation, maximum achievable market penetration, etc.) that have a significant impact on the forecast as a whole. As MCR began to develop initial forecasting models, we quickly found that the necessary input data to our calculations was either not readily available, not transparent enough to allow validation, or both. Therefore, we concluded that developing forecasting models based on adoption or S-Curves would require significant effort and would likely produce unreliable results.
As an alternative for developing the PV forecast, we examined several online tools and calculators, including Project Sunroof, Deep Solar and NREL’s dGen. From this review we concluded that these publicly available tools lacked adequate transparency and granularity for utility-specific forecasting.
Given the lack of confidence in either an S-Curve modeling or online tools approach, MCR conducted an extensive EV and PV forecasting methodology literature review that examined over 60 references on EV forecasting and over 30 sources on PV forecasting. Based on the review, we decided to use some well-known national forecasts of EV and PV adoption, and scale them to IPL’s service territory. The scaling was based on factors such as the installed base and historical growth rates of EV and PV in IPL’s territory, population, income, policy/regulatory considerations, etc. IPL agreed with the approach; according to Erik Miller, Senior Research Analyst, “It was a linear approach applying some other source data to create our forecast.”
Results
MCR successfully developed forecasts for numbers of EV and PV systems, EV and PV energy impacts and PV capacity impacts for the 20-year forecast horizon. We presented our results to the IRP stakeholder group; the results were generally well received. IPL will integrate MCR’s forecast with their native load and energy forecast to use in developing their 20-year IRP.

Richard Milward, Lead Consultant
Richard Milward is a Lead Consultant in MCR’s Energy Efficiency practice. He has over 20 years of electric utility industry experience in evaluating energy efficiency program impact in all sectors employing a variety of evaluation techniques; implementing and administering Strategic Energy Management (SEM) in industrial facilities; evaluating industrial and commercial SEM programs; empirical energy modeling using regression techniques for utility reporting; and teaching all varieties of technical, mathematical, and statistical concepts to trainees possessing a wide range of subject knowledge.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Melanie Gillette, Director
Melanie Gillette is a Director in MCR’s Energy Efficiency practice. She has over 25 years of experience in utility industry, demand response, energy efficiency and distributed energy resources policy as well as a strong background in project management. Melanie has led policy teams; formed strong industry coalitions; written legal briefs and expert testimony; advocated at numerous state commissions; managed large, multi-year efficiency and transmission projects; and represented a variety of interests within the energy industry.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
Undergoing cost reduction through risk informed budgeting for a large Southwest municipal utility
“The MCR team was very professional and very driven. I really appreciate their direct approach to engage executives and managers. Through the course of the project, I quickly came to trust their knowledge and conclusions of our business.”
—Chief Operating Officer
Background
A large municipal electric utility in the Southwest was challenged by the City Council to operate under affordability goals requiring them to limit electric rate increases to two percent per year while keeping customer’s electric bills in the bottom 50 percent of all electric utilities in their state. To achieve these goals, the utility needed to explore new ways to manage its spending in the most effective and efficient manner possible.
Historically, the utility’s business units developed budgets based on the previous year while adjusting for expected differences in the upcoming year. They examined operating expenses in the aggregate without the level of detail necessary for effective budget analysis. This approach limited management’s ability to drive significant, achievable and lasting benefits.
As the company entered their annual budget cycle, the Chief Operating Officer wanted more transparency and rigor in the budgeting process in order to identify areas for significant cost reduction. With significant O&M cost reduction as the goal, the Chief Operating Officer approached MCR for help.
Solution
MCR used its proven Risk Informed Budgeting (RIB) process to help our client reach its spending goals. At its core, Risk Informed Budgeting requires budget owners to justify all budget requests from a baseline of zero. In a sense, it is the antithesis of the more traditional incremental budgeting process, which embeds a continuation of the past without rigorous spending scrutiny.
We worked directly with our client’s management team and budget analysts, guiding them through our RIB process steps:
- Develop a budget item classification framework relating spending levels to specific safety, regulatory and reliability risk factors
- Discuss each budget line item and assign to the risk classification framework
- Facilitate a structured review process guiding senior managers towards a risk-based ranking of all their budget line items
- Facilitate a final ranking process forcing the delineation between line items above and below the target budget funding line
In team meetings, every line manager was asked to challenge their own paradigms of what spending was truly required to operate and maintain their organization. Nothing was taken for granted in the review and all spending was challenged. The approach ensured each line manager’s budget submission was prepared with detailed documentation and recognized facts to substantiate all proposed spending.
Results
MCR and the management team identified opportunities to save $15 million in O&M expenses (nearly 10% of the reviewed budgets). This reduction puts our client on a path to achieve its rate targets and meet the City Council’s affordability goals. In addition to the expense reductions identified by the RIB process, MCR also identified opportunities for operational improvements, including:
Information Technology
- Optimize the overall information technology portfolio by eliminating excessive legacy applications and controlling new application requests
- Reduce a significant number of contractors used as base load employees to operate and maintain key infrastructure
- Apply better software licensing controls to eliminate vendor-imposed penalties
- Establish a cloud / premise strategy to reduce and optimize application and data management costs
- Create a cost awareness culture among managers who were previously unaware of their actual performance to budget over the course of the year
- Improve project management controls to enhance scope control of many projects
Electric Service Delivery
- Reduce overtime used to complete regular maintenance when driven to do so by capital project work load. Rapid customer expansion drove capital workloads, which with limited resources, created a situation where overtime was used to address both capital and regular maintenance.
- Restrict overtime in project implementation with distant completion time horizons. For example, an LED upgrade initiative with a 5-year time horizon was partially completed using overtime.
Power Production
- Enhance power production management expertise in operating with an efficient budget and sharpening skills in effectively managing their costs
- Identify additional budget reduction opportunities management had previously not considered
Top 5 Features a Cost of Service Model Must Have (point of view)
In this era of increasing regulatory transparency and the need for innovation in rate design alternatives, utilities must have a state-of-the-art cost of service model to perform the necessary analyses. MCR recently conducted a survey of utility regulatory professionals on what they see as the “Top Five” key features that are required of today’s cost of service models. MCR’s Cost of Service model was developed to address these key features.
Download the Cost of Service point of view
Helping Duquesne Light Company serve the low income market by facilitating multifamily passive house projects
Download the Duquesne Light Company client story
Background
It is well known in the world of energy efficiency that it is particularly challenging to achieve energy and demand savings in the low income residential sector. Like many utilities, Duquesne Light Company offered a program focused on serving low income multifamily properties. After the winning bidder of the implementation contract abruptly withdrew from the contract, Duquesne Light turned to MCR to help implement the program internally.
It was clear from early discussions that there was growing interest within the region for Passive House designs and certification. Conversations with developers and other stakeholders revealed that the Pennsylvania Housing Finance Agency (PHFA) had adopted policies that awarded extra points in the selection process to projects that were Passive House certified. Additionally, PHFA had also required developers to seek out utility incentives and include those incentives when submitting the individual requests.
While there appeared to be a big opportunity in implementing Passive House projects, there were several challenges to overcome, including:
- There was no common definition of what “low income” means. The low income community operated under definitions based on percentages of area median income, while the regulated utilities used the Federal Poverty Guidelines.
- The Passive House model was not an approved model in the Pennsylvania state Technical Reference Manual (TRM), which meant that utilities could not accept the modeling results as given.
- Passive House models did not include any comparison to a “baseline” design. Energy efficiency savings in new construction projects were quantified by comparing the new building as designed and a comparable building built to be minimally code-compliant.
- Developers already made significant investments in two modeling efforts: 1) the Passive House model to achieve certification and 2) a sample-based, apartment-by-apartment set of models used to demonstrate code compliance. While the latter models included a comparison to code baseline, they do not include common areas; so the use of these models to quantify savings would leave significant savings on the table.
With this background and the goal of making the Passive House program a success, Duquesne Light relied on MCR to shepherd these projects through its existing Act 129 programs.
Solution
MCR began by working with both low income housing advocates and the utility’s independent evaluator to learn more about the background of Passive House design, certification, and its use within the state. MCR also worked with the statewide independent evaluator to determine whether Passive House models could be accepted by the Public Utility Commission (Commission). Having identified the challenges discussed above, MCR arranged for a meeting of representatives from the PHFA, Commission, and the regulated utilities to work on driving a common understanding of the issues and possible solutions.
Following this meeting, MCR developed an interim measure protocol to calculate savings by comparing the Passive House model to a separate whole-building baseline model. While this approach did not eliminate the need for multiple building models, it allowed developers to earn incentives and utilities to claim savings. These incentives and savings would be based on a comparison of the low energy use captured in the Passive House models with a baseline design modeled in an ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1 Appendix G-compliant software package.
Results
With this new approach, MCR worked with an interested developer who provided the necessary information and performed the modeling work. Most new construction projects within Duquesne Light’s commercial and industrial portfolio only considered the energy efficiency savings derived from lighting upgrades; by using our approach, MCR was able to derive savings and incentives from the whole project. In fact, 63% of the project’s savings were achieved due to the modeling effort (as show below).
The process of bringing these savings to fruition, from first encountering a Passive House submission to recording the savings, was not a short one. In fact, conversations with the developer began nearly two years before the project was completed. While a part of this duration reflected the realities of construction timelines, it also represented a sustained effort to find a way to fully incorporate the project within the utility’s program.
Over the course of two years, MCR engaged audiences well beyond traditional energy efficiency stakeholders, fostered intra-agency cooperation, and achieved significant savings in this hard-to-reach market.
Achieving cost reduction through risk informed budgeting for a top-10 municipal utility
Background
As part of an overall effort to inject more rigor into the development of their Operating & Maintenance (O&M) budget, a top-10 municipal utility in the Southwest sought to engage a firm with extensive experience in providing consulting services in risk informed budgeting (RIB) for utilities. The municipal’s desire was to implement a sustainable methodology to provide visibility into cost drivers, maximize each budget dollar, and help management ensure credible budget targets for the future.
Prior to the initiative to implement RIB, new budgets were created based on the previous year’s budget plus or minus any major events. This approach left the utility unsure of just how much they spent by necessity versus how much was spent out of precedence. With installed information systems, detailed analyses of budgets and actuals were difficult if not impossible to conduct.
A bid was issued in the form of an RFP seeking the most capable implementer of RIB for the budget cycle, as well as institutionalizing a complete RIB product incorporating a training program, desktop instructions, templates, processes, etc. After a highly-competitive process, including in-person presentations, MCR emerged as the clear choice to implement RIB for this large utility.
Solution
MCR used its proven risk informed budgeting process to help our client reach its spending goals. At its core, risk informed budgeting requires budget owners to justify all budget requests from a baseline of zero. In a sense, it is the antithesis of the more traditional incremental budgeting process, which embeds a continuation of the past without rigorous spending scrutiny.
The MCR team worked directly with our client’s management team and budget analysts, guiding them through our RIB process steps:
- Develop a budget item classification framework relating spending levels to specific safety, regulatory and reliability risk factors
- Discuss each budget line item and assign to the risk classification framework
- Facilitate a structured review process guiding senior managers towards a risk-based ranking of all their budget line items
- Facilitate a final ranking process forcing the delineation between line items above and below the target budget funding line
MCR facilitated sessions with every budget owner and their finance representatives to explore spending paradigms for every budget line item. Working with the client team, we challenged every proposed expenditure in terms of risk and controllability. In these discussions, when identifying the true drivers of cost, hearsay is not admissible. Documented facts with clear references are often necessary to break the paradigms of exactly what influence clients have on spending.
Results
Given the proper budget line item classifications, MCR and the client management team identified opportunities to save $80 million (25%) from the O&M request and $19 million (7%) from the previous year’s budget. These identified reduction opportunities enabled our client to meet their cost targets. In addition to the expense reductions identified by the RIB process, MCR also identified opportunities for improvements, including:
Operations
- For Power Generation, the complete discovery of reliability issues with low influence in scheduling, indicates long-term budget restrictions addressing reliability risk. Strategic decisions will balance the required investment to maintain reliability vs. the desired longevity of assets
- A review of various industry standard metrics in relation to T&D costs per mile, per customer, per kWh transmitted, etc. all seem to indicate the client has room for improvement
Financial & Treasury
- Current financial systems and processes will benefit from significant upgrades
- Changes to analyses and reporting will reduce significant labor constraints in this area
- Knowledge sharing would alleviate issues with considerable expertise residing in a few senior employees
Security, Safety & Fleet
- Security tech outsourcing for aging equipment maintenance needs to be balanced with asset management
- Enterprise Fleet KPIs need to include more cost-based measures
- Steps should be taken to lower the $/FTE training requests from Security, Safety & Fleet to better align them with the company and peer averages
Information Technology
- The core ERP system is overdue for an upgrade and re-implementation
- Technology is owned by many organizations outside of IT leading to conflict with the IT strategy; this issue could be remedied by bringing technology ownership under the IT umbrella
Developing transmission rate incentive filings at FERC for a joint action agency (FERC Filings)
“MCR is very good at explaining complex issues, which led to good, effective testimony … they were willing to take on challenges that I don’t think other consultants would be willing to do. Yet, they were able to help us stay disciplined and realistic about what strategies we should be willing to take on … with their help, we were successful attaining what many people in the industry considered precedent setting outcomes.”
—CEO
Background
A joint action agency decided to invest in a major new transmission project with other surrounding utilities. The economic advantages for its members, however, were dependent on receiving transmission rate incentives for the project, including a hypothetical capital structure, abandoned plant cost recovery, recovery of construction work in progress in rate base and the establishment of a regulatory asset for deferred costs. MCR was asked to oversee the filings.
Solution
We worked closely with our client and their Washington-based legal counsel on multiple required filings. MCR developed the filing outlines, drafted testimonies sponsored by the client and by MCR, and provided the required changes to the standard templates to implement the changes in the pro forma formula rate. MCR provided ongoing intervention support during the process, including mediation and settlement discussions with interveners, RTO tariff staff and FERC staff on select issues.
Results
The Commission issued very positive rulings. Mediation and settlement discussions led to agreements that were also favorable to our client. MCR and our client subsequently worked closely with the RTO to implement the rulings.
Providing cost of capital expert testimony for a joint action agency (FERC Filings)
“MCR created an innovative analysis based on our historical debt service coverage that compared to a traditional IOU ROE analysis, which allowed us to make a reasonable filing at FERC that was ultimately accepted.”
—Transmission Planning Manager, joint action agency
Background
A joint action agency was joining an RTO and anticipated making a Section 205 rate filing at FERC, which required an expert witness to support the requested return on equity (“ROE”) to be used in its formula rate. The joint action agency requested MCR to provide an analysis to determine the recommended ROE and support the recommended ROE with related expert testimony.
Solution
Prior to the Section 205 filing, MCR provided an innovative analysis that translated the client’s debt service coverage ratio into a requested ROE level. MCR shared the results with the client and assisted in the development of an overall filing strategy. As part of the Section 205 filing, MCR refined the analysis using updated data and provided the associated testimony to justify the recommended ROE.
Results
After settlement discussions, the client came to an agreement with multiple interveners regarding a number of issues, including the proper level of return. Ultimately, the parties agreed to the client’s desired level of debt service coverage, thus achieving a reasonable level of return. The client obtained FERC approval of the settlement.
Developing a Section 205 rate filing to change the formula rate template (FERC Filings)
“Their knowledge helped improve our collection of transmission costs through an adjustment to the tariff template, a strategy they developed and we were able to get implemented. It was a very helpful, innovative and unique solution to put us on a more even playing field with peer transmission owners.”
—Chief Financial Officer, joint action agency
Background
A joint action agency was faced with an under recovery of its transmission-related costs because the standard transmission formula rate was not appropriate for its particular business situation. The joint action agency requested MCR’s assistance to help increase recovery of these costs.
Solution
MCR identified a potential change to the standard template that would more fairly allocate common costs to the agency’s annual transmission revenue requirement (ATRR). The joint action agency decided to make a Section 205 rate filing at FERC to change their formula rate template and asked MCR to support them. MCR identified key filing issues to be addressed, researched supporting precedents and provided an initial draft of the testimony sponsored by the client and supporting exhibits. MCR worked with the testimony sponsor, the rest of the client team and their outside counsel to enhance the testimony.
Results
The filing encountered no protests and it was accepted by FERC through a letter order. As a result, the client was allowed to change its template, which resulted in recovery of hundreds of thousands of dollars of additional transmission costs each year.
Developing cost of capital expert testimony for joint action agency (FERC Filings)
“MCR’s cost of capital testimony was content-rich, succinct, and effective.”
—VP of Transmission, joint action agency
Background
A joint action agency formed a Transco in order to own transmission assets it had acquired from its members. As part of establishing the company, the Transco faced a number of contentious issues in its associated Section 205 FERC rate filing to establish its transmission formula rate. The Transco engaged MCR to provide expert testimony on one of the most critical issues in the filing: determining the appropriate level of cost of capital.
Solution
MCR first discussed the key issues related to the Transco’s cost of capital with client personnel and their outside counsel. MCR then conducted an analysis of debt service coverage ratios of joint action agencies, G&Ts and municipals typically required by credit rating agencies consistent with obtaining the Transco’s desired “A” credit rating. MCR subsequently drafted testimony that considered the completed analysis, other related financial issues in the case, FERC precedent, the Transco’s goals and MCR’s previous client experience. This testimony supported use of the requested margin requirement percentage (a form of return), using the cash flow formula rate template. MCR reviewed and discussed its draft testimony with client personnel and their outside counsel, and submitted the testimony as part of the Section 205 filing.
Results
Despite substantial intervention by neighboring IOUs, FERC agreed with the arguments of MCR’s testimony and approved the Transco’s filing and requested margin ratio. FERC cited MCR’s analysis related to required debt service coverage ratios, FERC precedent and issues unique to the case. Based on these highly favorable results, the Transco now has a FERC-accepted formula rate.
No End in Sight: Can Transmission Investment in MISO Continue at this Pace? (white paper)
There are many factors driving transmission investment. Just when one factor seems to run its course, another reason for investing in transmission takes over. In MISO, the growth rate of transmission investing over the last year has slowed a bit, but the absolute levels of investment will remain high for at least the next several years as investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) and transmission companies (“Transcos”) continue to see transmission investment as a major driver of earnings. Although transmission investment is broadening somewhat to more generation and transmission cooperatives (“G&Ts”) and municipal utilities, the message for public power and cooperatives in MISO remains clear: Investing in transmission is the most effective way to counter rising transmission rates.
Download the MISO Investment white paper
Helping Arizona Public Service Company implement MCR’s Cost of Service Tool to achieve greater cost transparency
“MCR was very responsive and very thorough. We’re continuously impressed with how quickly they were able to implement the model; it was much shorter than other vendors’ estimates. I think they did a tremendous job”
—Jessica Hobbick, APS Manager of Rate Design & Revenue Requirements
Background
Arizona Public Service (APS) began their search for a new cost of service model in 2017 at the end of a general rate case proceeding. The new rates sought significant structural changes with respect to net metering and other related issues. The nature of the changes prompted the input of many intervenors and intense review of their rate and cost of service filings. At the heart of the cost of service filing was an existing database tool. While the tool generated the appropriate reports for the filing in spreadsheet form, these reports were essentially pasted values with no underlying logic. Given the scrutiny of the filing, commission staff and intervenors sought more transparency on the logic, which the existing tool had buried in proprietary code. As part of the final rate order, APS agreed to implement a more transparent cost of service model.
Solution
APS selected MCR’s Cost of Service Tool (COST™) after reviewing various alternatives. COST™ met two important criteria for the utility per Jessica Hobbick, APS’s Manager of Rate Design & Revenue Requirements, “We were looking for something Excel-based, so intervening parties could make changes to see how the revenue requirement changes” and “we were looking for something that didn’t rely on as much vendor support, a living breathing model that we could change between rate cases.”
Results
The MCR team worked closely with APS staff to quickly implement COST™ with the new model up and running in a matter of weeks. COST™ met the requirement for transparency, allowing external party review of all model logic coupled with the ability to adjust key inputs. In addition, APS staff were able to quickly learn the model and incorporate modifications to meet ongoing changes in their rate structure.
FRST Webinar
Join MCR experts as they discuss MCR’s Financial Risk & Strategy Tool (FRST™), which is a Microsoft Excel-based application designed to handle critical utility planning needs. MCR is providing an online demonstration of FRST™ to review how our clients use the model to conduct long-range financial and rate forecasting.
Sign up for the date/time that works best for you!
- Tuesday, September 11, 1-2 pm EDT REGISTER HERE
- Friday, September 21, 12-1 pm EDT REGISTER HERE
Helping Duquesne Light Company train middle and high school students to become energy auditors who develop energy conservation measures in their own schools
“The Duquesne Light Community Energy Efficiency Education Program was created to inform students about how we get our power and how to be more conscious using it. We have touched upon these topics in class before, but this program provided students with a more in-depth look from the power company itself.”
—High School Senior, Central Valley High School
Background
Pennsylvania Act 129 requires electric distribution companies in the state, including Duquesne Light Company (DLC), to develop cost effective Energy Efficiency (EE) plans that would reduce electricity consumption across their service territory. In developing an EE plan, DLC wanted to design and offer a unique program that would get students and teachers involved in learning about energy use and how they could reduce energy consumption in their own schools.
Solution
MCR worked with DLC to design and implement the Community Education Efficiency Program (CEEP), which prepares middle and high school students to become Energy Efficiency Auditors. CEEP Energy Advisors and Lead Teachers provide students training designed to help them understand energy use and develop energy conservation measures in their own school. Using their student-prepared Energy Conservation Action Plan & Report, students implement their own energy conservation awareness measures to win prizes during a three-week inter-school competition. The program provides the schools cash incentives to offset the cost to implement energy saving improvements.
Results
The semester-long CEEP program was successfully completed at nine schools. Almost 200 students received an average of two hours of training per week for 15 weeks, resulting in 6,000 student hours of training. The students audited 285 school rooms, encompassing over 780,000 square feet. Focusing on lighting and computer loads, the students identified over 500,000 kWh in savings from simple lighting recommendations and another 2,000 kWh from computer phantom load reductions. Greater savings were identified that could be attained through HVAC and capital improvement projects.
As part of the program, students conducted a three-week campaign to encourage energy efficiency in their schools. The student-led campaigns included producing videos, hanging posters, and holding contests that challenged their fellow students and staff to reduce energy consumption. Many students engaged their family members to reduce energy use at home. In many schools, students presented information about the Student Energy Auditor training and audit results to school administrators. The administrators showed interest in continuing the student’s quest to reduce energy consumption and costs through capital improvements to school district buildings.
Conducting a valuation of transmission capacity rights (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“MCR looked at the valuation analysis from three very different angles and explained their final choice for valuation. No party contested any of the analysis.” — City Manager, municipal utility
—City Manager, municipal utility
Background
A municipal utility was contemplating leaving its joint action agency and wanted to determine the value of its transmission capacity rights if it were to sell those rights to another member of the agency. After conferring with industry colleagues, city managers of the two municipals engaged MCR to conduct an independent valuation analysis of the transmission capacity rights to establish a fair sales price.
Solution
MCR reviewed existing and previous contracts to fully understand the details of transmission capacity rights and how the transmission capacity rights could be transferred. MCR worked with the agency’s outside counsel to ensure proper interpretation of the contracts, leading to the appropriate set of modeling assumptions. MCR calculated the net present value (“NPV”) of the transmission capacity valuations using three different valuation methods and determined the most appropriate method given the specific circumstances. The NPV analysis was conducted over 30 years and over 15 years to assess the sensitivity to the forecast horizon. MCR presented its results, including an explanation of its methodology, to the city managers and to the agency’s outside counsel.
Results
MCR’s methodology and recommended valuation provided a framework and starting point for the two municipals and their agency to negotiate the terms of the sale of the transmission capacity rights. In the end, both municipals agreed on a value and were pleased with the outcome. They are now moving forward with the transaction. The selling municipal will be able to use the funds to reduce its long-term liabilities and the municipal acquiring the transmission rights will use the additional transmission capacity to help offset the transmission costs associated with substantial load growth.
Quantifying economic benefits of joining an RTO as a transmission owner for a municipal utility (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“MCR has an expertise that was otherwise very difficult or even impossible to find. MCR’s expertise has allowed us to move forward with our strategic plan on transmission. … MCR has become more than just a consultant; they’ve become a partner in our operation.”
—General Manager
Background
A municipal utility client was contemplating membership as a transmission owner in a Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) and asked MCR to provide an independent cost-benefit analysis of becoming a transmission owner. But first, the General Manager and Director of Finance wanted to make sure that the municipal was properly recording their costs in conformance with FERC accounting and would comply with the RTO’s new formula transmission rate protocols.
Solution
MCR worked with the client’s transmission and financial personnel to conduct a cost integrity review of the client’s assets and costs with a particular focus on data comprising the formula rate revenue requirement. MCR reviewed the recording of costs, made recommendations in cost reporting to optimize transmission revenue and conducted a client workshop. The workshop discussed the components of the formula rate template and allocators impacting revenues, highlighted the results of the cost integrity review and educated client staff on the requirements of the formula rate protocols.
Results
The results of the formula rate review fed into the cost-benefit analysis of whether to join the RTO as a transmission owner. MCR also worked with the client to define the key analytical assumptions. The analysis results were presented to the board of directors and helped our client define a long-term transmission strategy, which included joining the RTO as a transmission owner.
Transmission Spending in PJM: Are You Obtaining Your Share of Transmission Investment? (white paper)
In PJM, total transmission investment by investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) and transmission companies (“Transcos”) continues at high levels and is driving earnings. The factors encouraging investment show little sign of abating, ultimately leading to higher transmission rates. Many generation and transmission cooperatives (“G&Ts”) and public power entities are facing higher transmission rates from this substantial investment. Obtaining their own fair share of transmission investment can provide a means to mitigate the impacts of transmission rate increases and provide value to their members.
Download the PJM Transmission Investment white paper
Providing economic analysis of a proposed new transmission investment for a G&T cooperative (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“MCR takes complicated concepts and presents them in a way that’s easily understood by our Board of Directors, who are not immersed in the transmission industry. MCR has a confidence when presenting in front of others and that comes from knowledge, knowing the business, which is quite valuable.”
—Transmission Planning Manager
Background
A generation and transmission (G&T) cooperative was considering investment in a highly visible regional transmission project that had complicated cost allocation methods. The client asked MCR to lead the client’s working team in conducting an analysis of the economics of the project and whether there was sufficient value for its members.
Solution
MCR led a client working team through a series of meetings designed to identify key assumptions of the analysis, including the cost allocation assumptions, and to review the results of the analysis. MCR’s Transmission Project Evaluation Tool™ was used to conduct the analysis, which included Monte Carlo risk analysis, to contemplate varying levels of key inputs, such as the equity ratio from a potential hypothetical capital structure.
The analysis showed there was substantial net present value to the G&T’s members of investing in the project, under all relevant ranges of assumptions. In conjunction with our client, MCR help present the analysis results to our client’s Project Review Committee, the Executive Review Committee, the Distribution Cooperative Managers Committee and ultimately the Board.
Results
Using the results of the analysis, our client helped change the mindset in the company to one that more actively supported transmission investment. By proceeding with the regional transmission project, our client increased reliability and created incremental value for its members.

Jacob Hannan, Manager
Jacob is a Manager in the Energy Efficiency practice at MCR. He has over 10 years of experience in energy efficiency, data analysis, and research. His expertise includes demand side management (policy, planning, and management) and data science (wrangling, modeling, and visualization). He has served on the Planning Committee of DOE’s Technical Information Network for Solid-State Lighting, committees for the Consortium for Energy Efficiency, and several other national and regional organizations focused on energy efficiency.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
Transmission Investing in SPP: Are You Obtaining Your Share of Transmission Investment? (white paper)
In SPP, total transmission investment continues at high levels and is being driven by many factors. However, recent investment by investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) has been dominated by two IOUs. Many generation and transmission cooperatives (“G&Ts”) in SPP have recently stepped up their investment activity and some are now investing in transmission at a rate equivalent to their load ratio share, providing a means to mitigate the impacts of transmission rate increases and provide value to their members.
Download the SPP Transmission Investment white paper
Developing a transmission business plan for a G&T Client (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“I’m a return customer, because I think MCR really possesses an excellent understanding of transmission as a business and how to create value from investing in transmission. They were very useful in conveying those concepts and helping people apply those concepts towards building a concrete and actionable plan.”
—CEO, G&T
Background
A generation and transmission (G&T) cooperative faced increasing transmission rates and growing reliability needs of its members. The G&T asked MCR to lead an effort to develop a transmission business plan that articulated a clear vision and identified transmission investment opportunities that would enhance the reliability of cooperative members while also providing revenue that could partially hedge rising transmission rates.
Solution
MCR led a senior client working team through a series of team meetings designed to develop a Transmission Business Plan. MCR’s approach included understanding key transmission industry issues/trends and methods for creating value for its members, articulating a vision for the transmission area, developing key strategies, identifying specific transmission project opportunities for improving member reliability and creating financial value. The client identified projects for reliability improvements with MCR using its Transmission Project Evaluation Tool™ to conduct the financial analysis. Based on the client’s research and phone interviews with other utilities, the team also identified an initial set of reliability metrics to help focus the G&T’s reliability efforts. In addition, MCR assisted the team in identifying the transmission functions, staffing levels and capital investment required to run transmission more like a business.
Results
The financial analysis of various project opportunities showed there was substantial net present value to the G&T’s members of investing in transmission projects identified during the engagement compared to business as usual. Pending Board approval, the G&T intends to move forward with its Transmission Business Plan, including implementation of about a dozen strategies that will create value for its members through reliability improvements and revenue enhancement.
The New Tax Law: Will a Lower Tax Rate for IOUs Impact the Advantage Public Power and Cooperatives Have in Transmission Investing? (point of view)
The new tax law reduces the income tax rate for IOUs. What does that mean for public power and cooperatives when it comes to transmission investing? The enclosed MCR Point of View discusses the impact of the tax rate reduction on transmission investing and whether it will affect the relative cost competitiveness of public power and cooperatives compared to IOUs.
Download the tax law point of view
Providing analysis and negotiation support for a municipal utility (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“The negotiation process with the incumbent utility in our zone went very well. MCR’s modeling results proved we should be building the transmission substation in order to obtain investment neutrality. Without their expertise, we would not have been able to accomplish what we accomplished.”
—General Manager, municipal utility
Background
A municipal utility was preparing to conduct negotiations with the incumbent utility in its pricing zone over the construction of a large proposed substation that would nearly triple the net book value of the client’s total transmission investments. The pricing zone participants and our client faced rapidly rising zonal transmission rates. The client requested MCR’s help to determine whether it should be entitled to build the substation based on a desire to be neutrally invested in the zone (i.e., when transmission network zonal revenue offsets the zonal tariff paid). In addition to the analysis, the client requested MCR to participate in the actual negotiation meetings with the incumbent utility.
Solution
MCR conducted a thorough analysis of the financials of the proposed substation project. Prior to the negotiations, MCR produced a report for the client that discussed the assumptions and forecasted results of the neutral investment analysis. MCR and the client then prepared for and participated in a series of meetings and conference calls with the client and incumbent utility, including the legal counsels of each party, to review the results of the analysis and begin negotiations related to the substation. MCR worked closely with the incumbent to reconcile its results to the modeling results of the incumbent.
Results
The final reconciled results showed that MCR’s client was currently underinvested in the pricing zone and will continue to be underinvested even after they make the proposed substation investment. After reconciling the modeling assumptions, the incumbent utility agreed to the results, leading to a formalized substation construction agreement and an ongoing coordinated planning agreement between the parties. The planning agreement codified the goal of having our client be entitled to a level of ongoing transmission investment that will ensure it will be neutrally invested in the future, thus offsetting anticipated increases in zonal transmission rates.
Conducting an economic evaluation of an RTO membership (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“MCR guided us through considerations logically, so we could easily ask what would cause MCR to have a different opinion. They provided recommendations and rationale that was easy to follow… they help synthesize data in a manner that increased our industry insight. They connect and make relevant industry insight based on the audience’s or decision maker’s needs.”
—VP, municipal utility
Background
A municipal utility recently expanded its transmission system and expected continued significant transmission investment for the next several years. The client was interested in whether it made economic sense to place its transmission assets and generation into MISO and take network integrated transmission service (“NITS”) as a MISO transmission owner (“TO”). Currently, it serves its load with behind the meter generation and transmission and takes occasional point-to-point service. The results of this study would provide important input into the municipal’s broader integrated resource strategy and strategic plan goals. In addition to comparing the Base Case (the status quo) to the TO Case, the client also wanted MCR to run scenarios where two coal generating units were retired early and how that would impact transmission costs under the Base Case.
Solution
MCR used its RTO Evaluation Model™ to conduct a 20-year forecast of the Base Case, identifying the current MISO charges and the revenues associated with the client’s excess transmission capacity. This Base Case forecast was compared to the TO Case whereby the client placed the transmission assets into MISO, joined a joint pricing zone and obtained full revenue recovery of its transmission-related costs under MISO’s Attachment O formula rate. For the TO Case, MCR developed an annual transmission revenue requirement (“ATRR”) forecast using the MISO Attachment O formula rate template and projected the ATRR based on forecasted capital expenditures, capital structure, depreciation rate and return assumptions. The analysis included a forecast of all company transmission tariff costs, capital expenditures, load and zonal rates and considered the impacts of a grandfathered agreement applicable to certain load. MCR compared the net annual benefits of the Base Case to the TO Case to identify the forecast year where becoming a TO made economic sense (crossover year). MCR then ran the two early coal generating unit retirement scenarios to determine how operating with less behind the meter generation affected the net benefits and optimal timing to become a TO. MCR also ran a sensitivity based on higher load growth reflecting the potential for a large load addition in the near future.
Results
The analysis using MCR’s RTO Membership Evaluation™ concluded the municipal should delay joining MISO as a TO, as the net benefits under the Base Case were higher than the TO Case for at least the next several years. The analysis showed particular sensitivity to certain inputs, such as projected zonal NITS rates and excess transmission capacity, a portion of which could be resold. These factors and others such as load growth and capital expenditures indicated the client should revisit the analysis with updated assumptions in a few years. The sensitivity analysis indicated one of the early coal retirements had only modest impacts whereas the other coal plant had significant impacts on the decision to become a MISO TO and the optimal timing.
MCR Formula Rate Review (brochure)
MCR’s Formula Rate Review is beneficial in a number of ways. It ensures you are:
- Optimizing your ATRR in MISO’s Attachment O/SPP’s Attachment H cost template
- Able to withstand challenges from outside parties
- Can fully meet FERC and MISO protocol requirements
MCR has developed or reviewed over 100 formula rates for clients in SPP, MISO and PJM. Through this extensive experience, MCR has developed a Formula Rate Review to assess whether transmission revenue is being left on the table and whether your transmission-related costs are “bulletproof” against third-party scrutiny.
Conducting a review of the transmission formula rate and developing a transmission revenue forecast (Strategic Economic Analysis)
“I assumed the person before me knew what they were doing, so I was hesitant to change the way they were doing things. MCR opened my mind and gave me the confidence to change the way things are done.”
—Manager of Accounting & Finance, municipal utility
Background
A transmission-owning municipal electric utility in MISO was significantly upgrading its existing transmission assets while moving from point-to-point service to network integrated transmission service (“NITS”). Because of this, the municipal wanted to ensure the upgraded assets obtained full revenue recovery in the MISO Attachment O formula rate to help offset their upcoming NITS costs.
Solution
MCR conducted a three-stage process to ensure the client reached full revenue recovery for its transmission-related assets and expenses. First, MCR conducted a review of the municipal’s Attachment O formula rate and work papers and its detailed general ledger accounts, supplemented with interviews of key client personnel. This step ensured the client was recording its costs consistent with the FERC Uniform System of Accounts and the MISO tariff. Second, MCR conducted a forecast of their annual transmission revenue requirement (“ATRR”) with and without the upgraded transmission assets to determine the ATRR impacts of recommended changes to the recording of costs. Third, MCR worked closely with the client to develop required documentation and “the story” to ensure the upgraded assets would qualify as networked assets under FERC’s 7-factor test. Along the way and also in a workshop setting, MCR provided education regarding the proper recording of costs and use of allocators related to the Attachment O.
Results
The Attachment O Review resulted in changes to various recording of costs and modified timekeeping processes to ensure costs were recorded consistent with FERC accounting. The client achieved a substantial increase in transmission revenue by placing its existing transmission-related costs in the proper categories and ensuring field personnel were charging the proper accounts. MCR’s forecasted ATRR with the upgraded assets provided an initial blueprint for a future formula rate submittal and was used by the client as an input to the municipal budget. After the client and MCR developed the required 7-factor test documentation, MISO performed a power flow study and accepted the upgraded assets as being networked assets eligible for full transmission revenue recovery in the Attachment O. The Attachment O Review resulted in a more educated and confident staff that now has a more in-depth understanding of Attachment O related assets and expenses and how allocators impact revenue, providing staff with the ability to make more informed business decisions going forward.
The Transmission Arms Race Continues: Are You Obtaining Your Share of Transmission Investment (white paper)
The “arms race” for transmission investments continues. In addition to investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) and transmission companies (“Transcos”), generation and transmission cooperatives (“G&Ts”) and public power in MISO are increasing their levels of investment. But in many cases, G&Ts and public power make transmission investments at a disproportionally lower percentage than their load ratio share. This mismatch results in substantial exposure to transmission rate increases for their members and customers. In order to mitigate the impacts of these transmission rate increases, public power and cooperatives need to focus on how transmission investing can create value for their members.
Download the Transmission Arms Race white paper
Comparing transmission cost and rate competitiveness (Transmission Cost / Rate Competitiveness)
“MCR has the full package; MCR brings the subject matter expertise and knowledge of transmission rates, rate structure, finance & accounting, and FERC policy.”
—Senior VP, cooperative
Background
A cooperative’s transmission rates had been escalating at a higher pace than the average of other transmission owners in the RTO. A senior vice president of the cooperative engaged MCR to compare their transmission-related costs and resultant rate to those of a peer group of neighboring utilities to understand the current and projected rate gap and the drivers of the cost differences.
Solution
MCR drilled down into the client’s transmission-related costs to conduct a comparison of cost components and determine the areas where the client’s costs were higher than the peer group. Costs comprising the transmission rate were scaled per dollar of transmission plant and as components of the client’s annual transmission revenue requirement (“ATRR”) to determine the high-cost areas and identify those costs having the largest impact on transmission rates. MCR also developed a five-year ATRR and transmission rate projection for the client compared to the peer companies using publicly available information for each peer. This projection illustrated the size and trajectory of the transmission rate gap between the client and the peer average.
Results
The Transmission Cost and Rate Competitiveness project led to the development of strategies to address the projected rate gap. These strategies included conducting a detailed transmission formula rate review that focused on ensuring all transmission-related costs were recorded in accordance with the FERC Uniform System of Accounts. As a result of the review, the client has made various changes in cost allocations and in the recording of costs to FERC accounts. The client has also identified other potential cost-reduction strategies to be implemented in the future to narrow the projected transmission rate gap. This effort also resulted in a more educated and knowledgeable staff related to the source of the costs populating the client’s formula rate and how these costs affect the client’s transmission rate.
Analyzing the rate impact of joining an RTO (Transmission Cost/Rate Competitiveness)
“They were very knowledgeable. That’s why we hired them; we wanted to tap into that knowledge. If they didn’t know, they would say they didn’t know. I got a great sense of integrity out of them as we went through the project.”
—Chief Financial Officer, G&T cooperative
Background
A G&T was interested in exploring the possibility of joining a major RTO in its region. The G&T wanted to know which of its transmission-related costs would typically be included in the RTO transmission rate in various pricing zones and how the RTO rate compared to the current transmission rate paid by their members.
Solution
MCR conducted an in-depth review of the client’s transmission costs to organize costs into a formula rate under typical RTO rules. MCR then forecasted the client’s annual transmission revenue requirement (“ATRR”) under different formula rate methods and calculated sample client network service rates and costs under different possible pricing zone scenarios in an RTO.
Results
MCR produced a detailed analysis for the client, which showed that moving to an RTO would mean a significant portion of their costs that are currently included in their own transmission rate would not be recovered in the transmission rate under typical RTO rules. The analysis also showed that the preferred template method (return on rate base or debt service plus margin) depended heavily on the forecast assumptions. Further, the results showed that if the client were to join an RTO, the pricing zone it joins would significantly affect the economics of future transmission investment. Lastly, the analysis led to an in-depth subsequent comparison of the client’s costs by FERC account compared to neighboring utilities.
Conducting a comparative capital investment analysis (Transmission Cost/Rate Competitiveness)
“MCR’s database and analytics were critical for us, as we lacked these capabilities in-house. MCR was given a specific task: to perform an analysis of historical transmission levels in key RTOs and then present their results and policy recommendations in supporting testimony that we planned to include as part of our comments in a FERC administrative proceeding. They delivered exactly what we were looking for, on schedule, and within budget.”
—Vice President, Government Affairs, Independent Transmission Developer
Background
An independent transmission developer was filing comments at FERC to a Notice of Inquiry (“NOI”) to support transmission incentives. The independent transmission developer engaged MCR to support two specific return on equity (“ROE”) incentives: the continuance of an existing Transco ROE adder and the introduction of a new ROE adder to encourage joint investment with public power and cooperatives.
Solution
In order to support the continuance of the Transco ROE adder, MCR provided a study comparing five investment-related metrics between traditional investor-owned utilities (“IOUs”) and transmission-only companies, or Transcos. The study covered IOUs and Transcos in MISO and SPP using data gathered in MCR’s Proprietary Transmission Investment and Load (“PTIL”) database. All five metrics, developed and analyzed by MCR, showed that Transcos had higher levels of investment than traditional IOUs over the comparison period of the last six years. MCR testimony concluded that the Transco business model has been effective in encouraging new transmission investment and that the key to Transcos’ superior investment levels is their management’s focus on transmission as a singular business function and ready access to capital, both hallmarks of a Transco.
In order to support the introduction of a new joint investment ROE adder to encourage increased joint investment between IOUs/Transcos and public power and cooperatives, MCR provided segment data comparisons covering MISO and SPP over the last five years for five key investment-related metrics. The analysis overwhelmingly showed that in all metrics, the combined IOU/Transco segment invested at a much higher rate than municipals and most generation and transmission cooperatives. The relatively low level of municipal and cooperative investment combined with their older facilities suggests that municipals and many cooperatives are faced with the prospect of declining reliability in the future. In addition to providing analysis of the metrics, MCR provided testimony explaining the reasons why municipal investment has been strikingly low. The testimony supported the introduction of a new ROE adder incentive for IOUs and Transcos to encourage joint investment with public power and cooperatives, leading to enhanced reliability of the grid.
Results
The conclusion from the MCR study of IOU vs. Transco investment was that the Transco ROE adder is working (i.e., encouraging transmission investment) and should be continued. Further, based on the investment comparison metrics in MISO and SPP for the municipal segment vs. the IOU/Transco segment, municipal investment is woefully lacking and FERC needs to incent further investment by public power by introducing a new joint investment ROE adder.
FERC is evaluating the comments from the NOI and will make its decisions regarding which existing incentives should be continued and/or which new incentives should be implemented (or examined further).
Running Transmission as a Business: How G&Ts Can Participate in Today’s Transmission Arms Race (white paper)
There has been an “arms race” for transmission investments among investor-owned utilities (“IOU”) and transmission companies (“Transcos”), resulting in substantial increases in transmission rates for all MISO pricing zones. By contrast, many generation and transmission (“G&T”) cooperatives have not increased their transmission investment at the same rate of growth, resulting in substantial exposure to transmission rate increases for their cooperative members. In order to mitigate these rate increases, a G&T needs to run transmission as a business and put in place a business plan and disciplines that focus on creating value for its members.
Download the Running Transmission as a Business white paper
Debt Management System: Specifically Designed for Managing Electric Cooperative Debt (brochure)
The typical electric cooperative can have hundreds of individual long-term debt issuances. Oftentimes, this leads to the creation of several disjointed spreadsheets throughout the organization, leaving it difficult to find the most up-to-date information on company debt.
MCR’s Debt Management System (DMS) provides a centralized database for storing, administrating and reporting an unlimited number of debt issuances.
Download the debt management system brochure
Debt Management System (brochure)
Typical electric cooperatives can have hundreds of individual long-term debt issuances. Oftentimes, this leads to the creation of several disjointed spreadsheets throughout the organization, leaving it difficult to find the most up-to-date information on company debt.
MCR’s Debt Management System is a single source database for inputting, tracking and reporting company debt, as well as dealing with complicating factors such as variable interest rates, swaps, repricing, weekend/holiday schedules and custom principal schedules.
Download the Debt Management System brochure
Advanced Life Cycle Management Planning: Building Confidence in the Future (white paper)
When asked, most nuclear utility executives say their organizations develop effective Life Cycle Management (LCM) plans. However, when analyzing industry data, a somewhat different story emerges as industry and regulatory groups continually flag deficiencies in LCM planning. A recent analysis of INPO Equipment Reliability AFIs found almost 25% were LCM-related. LCM is not new to the nuclear industry, but successful implementation appears to be a struggle for many licensees. How did the industry get to this point, and what can be done to fix it?
Download the Life Cycle Management white paper
Updating a unit of property catalogue for a government utility
Background
Recently a large southern utility, faced with improving reliability for an aging generation and transmission infrastructure, experienced ever increasing perplexity in decisions related to major equipment replacement accounting classification. First of a kind obsolescence projects further complicated accounting classification decisions driving the need for a review and revision of the company’s unit of property (UoP) catalogue. The UoP catalogue and capitalization policy determine if the cost of equipment replacements should be capitalized or expensed. A clearly defined catalogue created in accordance with FERC, GAAP and industry best practices simplify appropriate accounting classifications while minimizing the churn of capitalization decisions.
The utility enlisted the assistance of MCR to expedite completion of the catalogue review and update, ensure quality of the final deliverables and minimize overall cost. Project objectives focused around the development of a refined UoP catalogue to serve as the basis in determining capitalization of project costs. Leveraging benchmarking, in-depth understanding of plant engineering and strong financial analytics, MCR was able to successfully implement their new UoP framework.
Solution
A thorough review and update of a UoP catalogue was comprised of three stages:
- Benchmarking and Gap Analysis
- Catalogue Working Review and Update
- Capital Impact Analysis
As the project progressed through each stage, there was an opportunity for deep functional business unit involvement, generating discussion on current shortcomings and potential opportunities.
Benchmarking and Gap Analysis
- Quantitative analysis of materiality thresholds and capitalization practices at peer utilities formed the basis for the development of informed capitalization thresholds.
- Gap analysis of unique assets identified in peer catalogues provided insights on areas where the client catalogue required greater detail.
- Gap analyses were performed to pinpoint areas where unique assets identified in peer catalogues were not captured in the client catalogue.
- Comparison with peer catalogues typically identified major areas for improvement in terms of detail and catalogue organization.
- Bringing the utility in-line with industry best practice eliminated gaps in components, applied consistent criteria and supported a capitalization policy more accurately capturing material assets.
Catalogue Working Review and Update
- The project team worked in cooperation with the client to develop a database.
- Developed an MCR-supported database (integrated with client data), facilitates traceability of changes plus the reporting of current, added, removed or modified retirement units.
- Reviewed proposed changes with business unit personnel to confirm proposed changes, as well as to provide a forum to capture insights on upcoming projects and historical issues.
- The final database supported due diligence conducted to disposition new requests, closing catalogue gaps.
Capital Impact Analysis
- The UoP update project caused some changes in both the scope and frequency of capital projects on fixed assets as defined by the UoP catalogue.
- A capital impact assessment was performed to estimate the resulting shift in capitalization due to addition, deletion or modification of retirement units in the catalogue.
- Client input and MCR industry cost data were aggregated and evaluated with Monte Carlo analysis to produce best-estimate shifts between O&M and capital.
Results
Key project outcomes from the UoP Update Project were aligned with the three main project stages:
Benchmarking and Gap Analysis
- Detailed benchmarking of the client catalogue with the MCR industry catalogue resulted in a comprehensive view of where client capitalization thresholds fit in both national and peer sub-groups, which drove defensible capitalization policy recommendations.
- UoP count by major FERC account showed numerous catalogue gaps primarily characterized by level of detail, organization/classification (e.g. condenser/circ water boundaries), missing components, and erroneous FERC account assignment.
Catalogue Working Review and Update
- The project resulted in over a 30% reduction in the number of property units, reflecting the level of repetition and detail in the legacy catalogues. This success was achieved while simultaneously increasing asset coverage, giving the utility more flexibility and ease in its capitalization decisions.
- MCRs proprietary property unit account mapping produced a streamlined, implementable UoP catalogue, greatly decreasing contention and “churn” between Asset Accounting and the respective business units.
Capital Impact Analysis
- The impact analysis resulted in an anticipated (conservative) shift from O&M to capital spending of roughly $40M per year, a number that was analytically derived via Monte Carlo analysis drawing upon client and MCR cost data.
- As with all projects related to the manipulation of accounting treatment, great care was taken to ensure prudent, industry-supported changes to policy.
The resulting analyses and catalogue with supporting database were effectively transitioned to the client, initiating a planning phase to seamlessly integrate deliverables into the existing process.
Assisting Citizens Electric and Wellsboro Electric analyze their internal processes in preparation for customer choice in Pennsylvania for their customers
“MCR was always trying to understand our needs; they dovetailed into becoming a division of our company.”
—Craig Eccher, President, Wellsboro Electric Company
“Cindy [Menhorn] was an excellent witness; she came up with the questions and answers for the written testimony, and she was great during the cross-examination at the hearing.”
—Pam Polacek, Attorney, McNees Wallace & Nurick LLC
Background
In response to a Petition for Waiver, the Pennsylvania Public Utilities Commission (PA PUC) exempted Citizens’ Electric and Wellsboro Electric (the Companies), two investor-owned utilities in Pennsylvania, from having to implement an electronic data interchange (EDI) system associated with customer choice until 25% of their customers chose an alternative electric supplier. Although the percent of customers switching had not yet reached the threshold level required to implement an EDI system, the Companies wanted to proactively take steps in preparation for customer choice in their territories. The Companies asked MCR to facilitate a review of their processes and, if needed, develop a Request for Proposal (RFP) to solicit a third party vendor to implement the new EDI solution.
Solution
MCR worked with the Companies to review the requirements for PA PUC customer choice, PJM (the regional transmission organization) and EDI; assess the Companies’ existing billing system; develop a gap analysis and identify options for closing the gap. We also worked with the client team to create an RFP that detailed the business, technology and performance requirements to implement an EDI solution, and identify third party vendors whom could complete the requirements. MCR assisted in the evaluation of RFP responses and facilitated the selection of a billing system vendor. We provided benchmarked costs of systems with similar functionality to ensure that any action on the part of the Companies would serve their customers in a fair and equitable manner. MCR developed and sponsored expert rebuttal testimony on behalf of the Companies during their filing for a surcharge to cover costs associated with implementing the new EDI system.
Results
Our work laid a foundation that provides the Companies with guidelines and knowledge to implement the processes and systems necessary to provide customer choice within its franchised service territories. MCR’s process reviews included interfaces with the current billing system and external systems used by the electric generation suppliers and PJM. MCR assisted in the selection of the vendor for the customer choice EDI enhancements. A PA PUC Administrative Law Judge recommended in support of the Companies’ requested surcharge, which was based upon the least cost solution to the Companies, and MCR’s testimony. However, after reconsideration, the PA PUC decided the Companies would be required to request cost recovery in the next base rate case.
Assisting an investor owned utility provide reasonable rate options to its industrial customers
Background
A large electric utility had not filed a general rate case in more than 20 years. The industrial customers had been utilizing a real time pricing rate design and time of use tariff that had not changed in a number of years. In anticipation of a general rate case and a need to review rate alternatives with their large customers, the company requested MCR provide an overview of current rate alternatives, regulatory approvals, and an assessment of the utility’s rate menu for large customers.
Solution
MCR provided a pre-fling review of IOU electric utility large customer rates across the country, recent tariff changes, regulatory approvals and current “hot trends” for these types of customers. Working with the client’s pricing staff, MCR provided an assessment of tariff options currently being offered by the utility and alternatives that may or may not be included in the tariff options. In collaboration with the client staff, MCR also surveyed representatives of the large customer rate class on their experience with the existing rates and rates being offered to their companies’ facilities in other areas of the country.
Results
MCR was able to confirm and provide documentation showing the utility was offering the majority of rate options that other large customers across the country had available to them, giving the customer assurance the existing rate and pricing structure was still relevant. Our client was able to utilize this information in its general rate filing and during negotiations and settlement with the large customer participants in the rate case.
Capitalization Policy and Units of Property Integration (case study)
A large IOU operating in multiple jurisdictions faced challenges after merging with another utility; the existing Unit of Property (UoP) catalogues for the merged generation fleet, transmission, distribution and general utility property were burdensome and a constant source of debates in project capital and expense classification decisions. One senior accounting manager at the newly merged utility stated the UoP catalogues had become “out of control.”
Aligning the capitalization methods of both companies provided MCR with an opportunity to integrate industry best practices, discuss critical future projects and address unresolved organizational differences. IOU senior leaders also wanted to establish procedures to ensure the IOU could defend new levels of capitalization, should the public service commissions overseeing the company’s jurisdictions raise questions. MCR was asked to lead this project based on our prior experience with the client working on a UoP catalogue integration for a merger with a former utility.
Download the capitalization policy and UoP case study
Application Information
How to Apply
For immediate consideration, please e-mail or mail your resume to:
Carolyn Duffley
MCR Performance Solutions, LLC
155 N. Pfingsten Road, Suite 155
Deerfield, IL 60015
Bus. Tele: (847) 562-0066
E-mail: cduffley@mcr-group.com
An Equal Opportunity and Affirmative Action Employer
Thanks for signing up
A confirmation email will be sent shortly.
Improving an investor owned utility’s financial planning and risk analysis capabilities with FRST
“It was lightning speed ahead of our prior model. With FRSTTM, we could create more reports and more dimensions in a fraction of the time. There hasn’t been a need that’s come up that we haven’t been able to solve with FRSTTM.”
—Corporate Financial Analyst
Background
A mid-sized investor-owned utility was using an inefficient, “black box” planning model to develop their financial forecasts. The time required to manage the data inputs andgenerate reports was incompatible with the company’s goal to quickly produce alternative regulatory and financing scenarios. In addition, the company wanted to dramatically improve the flexibility of the financial forecasting process and efficiency of generating new forecasts. To achieve these goals, the company selected MCR to implement the Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRSTTM) financial planning model.
Solution
Working closely with our client, we tailored key features of FRSTTM to meet their financial and regulatory planning needs. Their previous database-oriented planning model created a complex array of output reports that were difficult to compare and contrast in a quick and useful manner.
We configured the construction module to allow specific assets to be associated with regulatory jurisdictions and enabled detailed forecasting of capital spending, including the impacts of renewables on the utility.
The regulatory logic incorporated automated revenue requirements calculations for state and FERC regulated jurisdictions. FRSTTM’s unique risk analysis logic was implemented for developing risk management scenarios. We also worked with the client’s staff to develop a scenario tool that compares multiple runs of the model and is flexible to allow changes in time periods and corporate entities.
Results
Our client was up and running with FRSTTM in just 8 weeks and their planning process was dramatically improved. The scenario tool we developed cut days off the time to generate scenario comparisons and the client is able to provide quicker turnaround of new forecasts with a significantly reduced staff. The risk analysis function provides senior management and the Board with a greater clarity around the potential variability of future financial metrics.
Enabling Georgia Transmission Corporation to develop better long range plans and forecast short-term liquidity with FRST
“The initial development and flexibility of FRST™ just blew us away. MCR knows far more about Excel than most people I’ve come across. They know how to put that into the context of our business model and tie everything together. With knowledge of utilities and experience in forecasting, developing the FRST™ model worked really quite well.”
—Dale Cooper, Assistant Controller
Background
Georgia Transmission Corporation was using a long-range financial planning tool that was difficult to maintain and presented significant challenges when a new calculation or a change in the business structure required model changes. In addition, the company wanted to improve their ability to test various scenarios and financing alternatives, and gain better insight to near-term liquidity. MCR was hired to implement a rapid Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRSTTM) deployment.
Solution
MCR completed the installation of FRSTTM in just four weeks. We implemented the FRSTTM long-range financial planning model, short-term liquidity model and a detailed debt forecasting tool. The liquidity model incorporates inputs from the debt tool, FRSTTM and financial actuals to provide a daily view of near-term liquidity. The debt tool contains a forecast of all the company’s debt issues and provides the journal entries for accounting on a regular basis.
Results
The FRSTTM model met Georgia Transmission’s financial planning goals. It provides the company’s planners with a structure to make quick updates to the base financial forecast and easily run alternative scenarios. The output reports meet the needs of the planning group’s key stakeholders, including the Board, ratings agencies and lenders.
Assisting an investor owned utility meet stipulation requirements for filing a future general rate case
Background
An investor owned utility in the Southwest needed to meet the requirements of a Stipulation resolving its last rate case before filing a future rate case. The Stipulation required the design of rates and cost allocation mechanisms for certain large commercial and industrial customers. Needing an outside expert to lead and facilitate the process, the company asked MCR for assistance.
Solution
We worked with our client on several key items, including developing an analysis of the rate impact and rate studies, as required in the Stipulation, for discussion with the customers. The analysis compared the rate designs using embedded and marginal cost studies as the basis. We prepared rate options and facilitated discussions with customers to solicit their input and gain alignment on issues, including appropriate seasonal and time-of-use peak periods, load shifting and energy efficiency disincentives.
Results
The requirements of the Stipulation were completed and the client received favorable feedback from the customers about the rate design meetings. The project positioned the client to focus on addressing its greater upcoming issues involving generating resource mix, cost allocation and revenue requirements for its upcoming rate proceeding.
Helping Southern Minnesota Municipal Power Agency improve financial planning processes and better manage funding and reserves using FRST
“In order to properly configure the FRST™ model, MCR had to thoroughly understand our drivers and business model. It never ceases to amaze me that MCR staff quickly figured out our business model.
There’s no doubt FRST™ has enabled us to have a much better handle on our financial metrics and requirements, and the ability to articulate those requirements to the Board and to regulators.”
—John Winter, Director of Finance and Accounting
Background
Southern Minnesota Municipal Association (SMMPA) was using an outdated, database-oriented financial planning tool to develop its long-range financial plans and rate forecasts. The planning tool was a “black box” system that required the system vendor to make all logic changes. In addition, the tool required manual loading of production cost forecast data, which created bottlenecks in the planning process as well as potential for data input errors. With the goal of fixing these planning issues and improving their ability to quickly create and analyze asset and financing scenarios, SMMPA asked MCR for help.
Solution
MCR worked with SMMPA to install the Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRSTTM) financial planning model. The base planning model was implemented in just eight weeks and included seamless integration with SMMPA’s production cost model, financial accounting system and other input sources. We developed a customized financing capability to enable specific bond funding for unique categories of capital spending. Additional financing logic was implemented to allow planners to target the use of reserve funds under various scenarios.
Results
The FRSTTM model has significantly enhanced SMMPA’s financial forecasting capabilities. The company’s planners can now make model logic changes without relying on an outside vendor. The planning process is more efficient with automated interfaces for production cost, accounting and other sources of data. Planners now have the custom financing capabilities they need to enable the company to plan funding and reserves that reflect how they manage the business.
Supporting Duquesne Light Company to design, file and implement energy efficiency programs to meet its Pennsylvania Act 129 obligations
“MCR’s assistance helped us design and receive PA PUC approval to run a portfolio of programs that achieved one of the State’s lowest acquisition rates ($0.12/annual kWh) and highest cost-effectiveness (portfolio TRC test ratio 3.1:1). This is remarkable given that we have Pennsylvania’s lowest avoided cost.”
—Dave Defide, Manager of Customer Programs
Background
Signed into law by Governor Ed Rendell in 2008, Act 129 required Duquesne Light Company, and other electric distribution companies in Pennsylvania, to develop cost effective plans that would reduce electricity consumption across their service territory by 1 percent by 2011 and 3% by 2013. In order to meet these requirements, Duquesne Light selected MCR to design and file an energy efficiency plan.
Solution
MCR worked with our client to develop an energy efficiency potential forecast and a portfolio of 17 energy efficiency and demand-response programs serving the residential, low income, commercial, industrial and governmental customer sectors. Working with the regulatory and legal team, we developed the plan filing, developed and sponsored expert testimony and participated in negotiations with the Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission (PA PUC) and Staff.
Results
The plan was approved with the proposed programs and funding. During program implementation, we provided our client with assistance in facilitating stakeholder meetings and managing relationships with the PA PUC and staff, key customers, customer groups and evaluation, measurement and verification (EM&V) evaluators.
Duquesne Light achieved its energy efficiency savings ahead of target, attaining energy efficiency reductions of 521,000,000 kWh (123% of goal) through the end of the program on May 31, 2013. Duquesne Light also achieved peak demand reductions that were 4.5% of peak load. Portfolio EM&V realization rates exceeded 95% as measured by an independent evaluation contractor and confirmed by the PA PUC Statewide Evaluator.
Becoming a More Effective Witness Course (brochure)
MCR provides services to enhance our clients’ abilities to present and advocate their positions in regulatory proceedings. MCR educators pull from their own experiences presenting and supporting expert testimony on behalf of clients before numerous state regulatory bodies and FERC. Additionally, MCR conducts seminars, workshops and mock trial training exercises to enhance the effectiveness of rate departments and in-house fact, policy and expert witnesses.
Our program, “Becoming a More Effective Witness,” provides a comprehensive approach to developing and refining communication skills. It combines classroom instruction, workshop activities and mock hearing experiences. The class addresses the theory, application and practice of effective witness skills and techniques. It also provides practical guidance to prepare and present every phase of testimony. “Becoming a More Effective Witness” focuses on the unique challenges of presenting testimony before a regulatory body.
Download the witness effectiveness course brochure
Helping a natural gas utility in the Southeast achieve its rate adjustment goals and prepare its staff for work on future proceedings
Background
A natural gas utility in the Southeast provides natural gas distribution services to more than one million residential and business customers in a three-state territory. Facing a revenue shortfall in one of its utilities, the company was considering a state regulatory proceeding to adjust its rates and other terms of service. The utility’s regulatory staff, while very capable, had various levels of experience in rate and regulatory proceedings. With the objectives of achieving a desired regulatory outcome and building on the existing skills and experience of its internal regulatory staff, the utility asked MCR for assistance.
Solution
MCR worked with the client’s regulatory team and legal counsel to develop an overarching framework for the case, prioritize and address key issues, develop structure and strategy of supporting studies, and draft and refine testimony and exhibits. We also assisted in performing rate case support functions by managing the flow of interrogatories, discovery requests and responses, and the filing of schedules and work papers. In working closely with the client’s internal regulatory staff, we served as process coach and advisor, and provided “hands on” training in all aspects of the proceeding.
Results
As a result of our work, our client reached a settlement on the rate case and achieved its desired regulatory outcome. Our work with the client’s internal staff helped transfer our knowledge and expertise in regulatory strategy and the regulatory process. With that knowledge, the client’s staff is now much better prepared to work on subsequent rate cases across all of its jurisdictions.
Contemporary Ratemaking Course (brochure)
A number of MCR’s clients have expressed a need for a comprehensive ratemaking course for their internal regulatory teams. While there are certainly a number of existing alternative rate classes to choose from, they don’t always fit a utility’s needs because they:
- Lack a utility focus
- Include consumer advocates and commission staffs as participants and presenters
- Tend to be rather expensive, especially when travel costs are considered
- Use a one-size-fits-all approach that is not well suited to a specific utility’s needs
MCR’s “Contemporary Ratemaking” training course addresses the issues mentioned above and helps our clients increase their staff’s understanding of the regulatory process and enhance their skills in becoming better cost of service and rate design professionals.
The course is customized to meet our client’s specific needs, including those from rates, legal, accounting and operations. Some of the participants are relatively new to rates and regulation and others are more experienced. To meet the needs of both, the course is held over multiple days and is designed to cover the fundamentals, advanced ratemaking and hot topics.
Download the contemporary ratemaking course brochure
Helping Duquesne Light partner with key customers to achieve significant energy savings through retro-commissioning programs
“I have been involved in hundreds of projects; I’m totally impressed with MCR’s ability to understand scope and bring things together; they really make life easy for me. I absolutely couldn’t be any happier. UPMC could not be any happier.”
—Drew Chidester, Energy Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Centers
Background
Duquesne Light Company faced different options for implementing its portfolio of energy efficiency programs recently approved by the Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission (PUC). Many programs were suited to be delivered by third-party “conservation service providers” through standard contracts. The company, however, was apprehensive about turning over all of its customer relationships to third-party contractors. MCR was asked to assist in identifying and managing key commercial and industrial (C&I) customer projects.
Solution
MCR analyzed Duquesne’s C&I customer base and recommended that it retain its long-standing relationships with key customers in the health care, education and public agency markets. We assisted our client in developing a partnership framework and engaged a key customer to undertake retro-commissioning projects at five major hospitals. MCR provided technical expertise on the projects, assembled and managed implementation teams, and developed documentation packages to support evaluation, measurement and verification (EM&V) of the projects.
Results
The projects were successfully completed, resulted in substantial savings and improved the client’s already strong business relationship with this important customer. The five hospital projects resulted in cumulative annual savings of over 13 million kWh and nearly $1 million in electric bills.
Cost Allocation for the Midwest ISO. ATRR Whac-a-Mole? (white paper)
Cost allocation of transmission investment costs continues to be a major obstacle to building large new transmission and achieving renewables generation goals in the Midwest ISO (MISO) region. Existing methods of cost allocation can result in disproportionate impacts on certain utilities in close proximity to new transmission, so new methods of cost allocation are being proposed. Like the carnival game of Whac-a-Mole, any particular cost allocation method that eases the annual transmission revenue requirement on some MISO regions or utilities will inevitably burden other MISO regions or utilities.
Download the MISO cost allocation white paper
Optimizing Program EM&V Results at Duquesne Light Company (case study)
All energy efficiency professionals know it is challenging to design a portfolio of energy efficiency programs that will withstand tough scrutiny by third-party evaluators and achieve high realization rates. But, you can achieve that goal with high cost effectiveness if you follow our guideline: Programs designed to be measured … measure well. MCR’s case study explores the methods for creating a portfolio of programs that feature evaluation at the core of the program design.
Download the Duquesne Light Company EM&V case study
Helping a large dual unit station achieve significant reductions in O&M costs
“In just this year alone, the MCR project results have yielded $8.7 million (10%) in non-outage related savings that will be repeated year after year. Our goal is to achieve cost performance on par with the number one performer for plants our size. If we keep working on these initiatives, if we’re not number one, we’ll be pretty darn close.”
—Chief Nuclear Officer
Background
A large dual unit station operates in a very challenging market in the west. Energy prices in the market are low at the margin, and are driven by substantial tax-subsidized wind generation and an abundance of low-cost gas-fired generation. As a result, profit margins for the station have become very narrow. The Chief Nuclear Officer of the station, knowing he needed to reduce O&M costs in order to become more competitive in the market, asked MCR to help.
Solution
MCR conducted an initial benchmark analysis focused on four major areas with opportunity for cost reductions. Informed by the benchmark, we guided the station’s cost center owners through our zero-base budgeting process. Using our cost analysis templates and supporting database, we worked with the cost center owners to analyze, challenge and risk rank every line item in the 2015 budget. Based on the risk ranking, we identified costs that could be reduced or eliminated from operations. Reflecting the cost reductions, the revised budget was consolidated, reviewed with the station’s management team and presented to the station owner’s Board.
Results
MCR and the station’s team identified opportunities to reduce non-labor O&M costs by 10% on top of substantial cost reductions implemented in the previous year. In addition to the savings, the new 2015 budget plan now includes a justification of every expenditure and a better understanding of the potential risks of not funding any specific budget line item.
Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool
 Download the FRSTTM brochure for municipals
Download the FRSTTM brochure for municipals
Download the FRSTTM brochure for G&T cooperatives
Download the FRSTTM brochure for distribution cooperatives
Download the FRSTTM brochure for IOUs
MCR’s Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™) is the forecast model of choice for finance and regulatory professionals who want a sophisticated planning tool that is easy to operate without the overhead, software coding and expense of proprietary “black box” models on the market.
FRST™ is written in Excel with a unique structure that manages large amounts of data, yet requires no coding, and allows users to quickly change the model’s logic and reports to address changing business needs. With its flexible data loading and mapping function, users can easily load data from budgeting, general ledger and capital asset systems; and FRST™ seamlessly integrates with production cost and gas supply planning models.
Clients often cite the FRST™ reporting feature as a favorite element of the model. It has the ability to define a virtually unlimited number of time periods and levels of detail for analyzing financial and operating data. Analysts can quickly compare the results of multiple planning scenarios and perform variance reporting of budget vs. actuals and budget to forecast.
FRST™ has a unique approach to regulatory analysis, allowing a high degree of flexibility. The model calculates revenue requirements based on key drivers and identifies the need for potential revenue changes. The easy-to-use regulatory planning panel allows for historic and future test years with movable test periods and rate effective dates. Analysts can quickly adjust ratebase, costs and revenues based on the most recent rate case or test new assumptions.
Why our clients choose FRST™…
- Open, flexible model
- Fast processing
- Robust reporting & analysis
- Wide variety of rate calculation options
- Knowledgeable consultants
- Easy to work with consultants
- Fast implementation (less than 8 weeks)
- Value (1/3 the cost of the competitors)
What our FRST™ clients are saying…
“It was lightning speed ahead of our prior model. With FRSTTM, we could create more reports, more dimensions in a fraction of the time. There hasn’t been a need that’s come up that we haven’t been able to solve with FRSTTM.”
“We liked that FRST™ is Excel-based and has the balance sheet and cash flow forecasting. Anyone can own it, so we could easily make changes within Excel.”
“We use FRST™ for executive management purposes in terms of looking at strategic issues, looking at financial information to provide credit agencies, earnings outlook for investment analysts. It is our budgeting tool from an income statement perspective.”
“MCR has a great product and delivered exactly what we needed. They have a skillset that’s unique to the utility industry.”
“There’s no doubt FRST™ has enabled us to have a much better handle on our key financial metrics and requirements, and to be able to articulate those requirements to the Board and to regulators.”
“The initial development and flexibility of FRST™ just blew us away. With MCR’s knowledge of utilities and experience in forecasting, implementing the FRST™ model worked really quite well.”
FRST™ supports electric, natural gas and water utilities. To learn more, download the brochure that fits your corporate structure.
Enabling a G&T utility to save millions and maintain its credit rating with an optimal environmental capital plan for its large coal units
Background
A generation and transmission cooperative (G&T) in the Midwest faced declining liquidity and deteriorating financial ratios, which put their credit rating at risk. The problem was compounded by the need for large capital expenditures to address NOx, SO2 and mercury compliance for its fleet of coal units to meet the Clean Air Transport Rule/Cross State Air Pollution Rule and the MACT rule. With a senior management mandate to develop lower-cost environmental compliance solutions in the face of capital constraints and projected rising member rates, the G&T asked MCR for advice.
Solution
MCR led a cross-functional team of client staff in using our business case process to evaluate costs and risks of various environmental compliance alternatives for the G&T’s two largest coal-based power plants. We helped the team gain consensus on the key background facts and specific quantitative compliance requirements, leading to a more precise problem statement and scope of the analysis.
We defined the base case and alternatives, including key cost and risk assumptions under different regulatory scenarios, and performed analysis to quantify the present value of costs and the risks of each potential compliance alternative, evaluating the tradeoff between cost and risk. MCR and the client team presented the results and recommendations to the client’s Project Review Team and senior management.
Results
The client implemented the recommended plan to install lower cost hybrid SCR/SNCR scrubbers to address NOx, change its fuel mix, purchase allowances and implement ACI for mercury. The plan saved $50 million, as compared to the base case solution of installing much more costly SCRs, and helped the G&T maintain and eventually raise its credit rating as financial ratios improved significantly without substantial member rate increases.
Reconcile Safety and Reliability with Cost: A Proven Approach to Optimize Project Spending at Nuclear Power Plants (white paper)
Most nuclear plants require some form of business case before a significant project is approved. These business cases, however, often “just go through the motions,” resulting in higher than necessary budgets and crowding out other important projects in the portfolio. A successful business case and project review process requires an active Executive Review Team and robust business cases to quantify alternatives and structure evaluation of cost-risk tradeoffs. This process helps ensure power plants meet their reliability goals in the most cost-effective manner. Moreover, when led by senior plant management, this approach can produce cost savings of 20%-60%, thereby reducing the strain on power plant capital and operating budgets.
Download the project spending white paper
Developing Robust Business Cases. A Proven Approach to Optimize G&T Capital Budgets in a Tight Credit Market (white paper)
G&T executives are facing increased pressure to reassess capital expenditure levels in response to the recent credit crunch and a slowing economy. However, requirements remain to build additional generation, new transmission and address environmental regulations. The challenge is to optimize and reduce capital spending in this environment in a systematic fashion that recognizes cost-risk tradeoffs. For many years, utilities have used some form of a business case to analyze and review projects before they receive funding. However, for most participants, this approach has become too much of a just go through the motions exercise. To be effective, the business case approach needs to become much more robust and useful to the engineers putting the cases together and to the senior management team needing to make the difficult capital allocation decisions.
Download the G&T business cases white paper
Energy Efficiency Program Management and Reporting Systems (white paper)
Running a portfolio of energy efficiency programs is a data intensive business. Baseline and replacement technologies, measure lives, deemed savings, budgets, program and cost effectiveness tests results: these represent a small sample of the energy efficiency business information. The users of this information are diverse and support a wide range of processes, including program management, regulatory reporting and customer relationship management.
Having accurate, timely and accessible data is critical to running an energy efficiency portfolio. However, MCR`s research suggests there is no standard set of data management strategies or software systems to manage this important business information. Instead, a wide range of incomplete solutions are being used across the industry.
Download the EE business management systems white paper
Helping an investor owned utility develop strategies to address the opportunities and threats of distributed generation
“When we engaged with MCR, there was a fundamental process and fundamental deliverables, but they didn’t presume any answers. They facilitated brainstorming with the executives, which I thought was very useful. They had a broad comprehension of the many different things happening in the industry to be able to dig deeper into ideas that participants presented.”
—Director of Strategy
Background
Like many investor owned utilities, MCR’s client faced a rapidly changing market environment driven by the emergence of distributed generation (DG) technology. This technology posed the threat of fundamentally changing the company’s business model, yet also represented an opportunity to develop new products and enter new markets.
Solution
MCR worked with our client to define four alternative future scenarios for their electric market. From these scenarios, we developed a set of “no regrets” strategies that made sense to pursue under any of the four scenarios. We then assessed a series of strategic options that represent a “strategic bet” for the company – bets that were likely to pay off under only one or two of the scenarios. The “no regrets” and “strategic bet” scenarios were incorporated into the client’s overall strategic plan.
Results
The results of our work provided our client with important intelligence about the threats and opportunities surrounding the evolving DG market. With informed strategies in place, the client is developing plans to conduct a launch of their own portfolio of DG products. Plans are also being implemented to address the regulatory and legislative issues surrounding the transition to a new business model.
Capitalization Policy and Units of Property Integration (case study)
Upon completing its merger with another utility, a large, multi-jurisdictional IOU needed to integrate its capitalization policies and unit of property (UoP) catalogues for its expanded generation fleet, transmission, distribution and general utility property. The existing UoPs were overly cumbersome and a perennial source of disputes in project capital/expense classification decisions. As one senior accounting manager at the company described, the UoP catalogues had grown “out of control.”
The merger presented an opportunity to align the capitalization practices of both companies, incorporate industry best practices, address key upcoming projects and resolve previous organizational disputes. Senior management also wanted to ensure any new levels of capitalization would be defensible to the public service commissions overseeing the company’s numerous jurisdictions. MCR had previously worked with the company on a UoP catalogue integration for its merger with a former utility and was asked to assist again.
Download the capitalization policy and units of property integration case study
Financial processes and systems: Custom power billing for Buckeye Power
“We thought our problem was unsolvable. MCR showed us a methodical approach to our problem. They showed us that not only could our problem be solved, but that a tool could be developed to address our problem. We were impressed from the beginning.”
—Jim Palmisano, Chief Accounting Officer
Background
Buckeye Power, Inc. is a generation and transmission cooperative that is jointly owned by 25 electric distribution cooperatives in Ohio. The company has its own generation and transmission contracts with five investor-owned utilities to deliver its power to over 450 substation delivery points. Buckeye used a complex system of text files and spreadsheets for capturing meter data and billing its cooperative members. The system was inefficient, prone to data errors and required significant staff hours to manually produce and review the monthly power bills. With the current challenges and new billing requirements on the horizon, the Chief Accounting Officer knew the current power billing approach and system was no longer viable and asked MCR for help.
Solution
We worked with our client to develop an assessment of its current monthly billing data, analysis processes and supporting systems. From the assessment, we developed recommendations for improving the billing process and created a detailed functional and technical specification document for a new power billing system. After researching the market for an “off the shelf” solution to meet the specification, the client team determined that a custom solution was the best option.
Results
We developed and deployed a custom power billing system for our client in four months. The system contains interfaces to import the various load management data, generate the invoices and supporting reporting to the Buckeye member’s website, and post the final billing transactions to the Buckeye accounting system. MCR’s power billing system eliminated the manual production and mailing of bills, and reduced the total cycle time to produce bills from 20 days to 7 days. Staff productivity was increased as staff hours required to produce bills were reduced from 160 hours per month to 40, all while greatly increasing the billing accuracy and availability.
Financial processes and systems: Integrating capitalization policies and units of property for a large utility merger
“The new unit of property catalogues are used daily by our accountants and engineers. The catalogues are better organized, more user friendly and are written in a language that field personnel can understand. MCR took out the confusion and created a logical, well thought out system.”
—Director of Accounting
Background
Upon completing its merger with another utility, our client needed to integrate its capitalization policies and unit of property (UoP) catalogues for its expanded generation fleet, transmission, distribution and general utility property. The merger presented an opportunity to align capitalization policies, incorporate best practices and resolve previous organizational disputes. MCR had previously worked with our client on a UoP catalogue integration for its merger with a former utility and was asked to assist again.
Solution
Our review of legacy UoP catalogues from both companies highlighted differences in the level of detail and component listings in multiple accounts. Functional areas became candidates for uniform application of capitalization guidance.
Referencing our capitalization best practices database of industry peers, we developed a solution to simplify the catalogue and provide more consistent guidance in classifying expenditures for capitalization. Finally, we developed an impact assessment to determine if there would be a shift between capital and O&M expense classification.
Results
The project resulted in an 80% reduction in the number of units of property. The new common units of property, along with well-defined capitalization thresholds and a user-friendly catalogue structure, simplify guidance for site organizations and reduce accounting staff time needed to analyze capital funding requests. The impact assessment estimated a minor shift in classifying expenditures from O&M to capital, easing management’s concerns about the level of capitalization in the newly merged entity.
Privacy Policy
MCR Performance Solutions (MCR) collects information on this site that enable us to communicate with and tailor our offerings to our clients and other interested parties. Our site’s registration and contact forms require visitors to give us information such as name, email address, phone number, and mailing address. MCR is the sole owner of the information collected on this site. MCR will not rent or sell the information collected through this website to any third party under any circumstances. MCR will periodically send notices of events, articles, and activities that may be of interest to our client community.
MCR’s website may be linked to third-party websites. MCR is not responsible for the privacy polices or content of any site to which we link. MCR has adopted this policy with the recognition that Internet technologies are rapidly evolving. Accordingly, our policy may change. Any changes will be posted on this page.
Questions about this privacy policy should be directed to the MCR website manager, info@mcr-group.com.
Site Map
Register – Registration
[pie_register_form]
Forgot Password
[pie_register_forgot_password]
Profile
[pie_register_profile]
Improving long range planning processes and systems for the operator of a large nuclear fleet
“We have benefited greatly from MCR’s unique skill set. Their understanding of the business combined with knowledge of our processes and tools along with extensive IT expertise have proven invaluable. MCR’s vision and leadership have greatly contributed to the effectiveness of our planning process and continue to move us forward.”
—Lead Engineer, Corporate Finance
Background
An operator of multiple nuclear facilities had a vision and master plan to sustain the business and achieve excellence by supporting good near-term operational decisions and laying the groundwork for long-term success. A key component of the master plan was to create a strong business planning culture across the nuclear fleet and overhaul its long range planning processes and tools.
Solution
MCR worked with our client’s nuclear engineering and business personnel to identify improvement opportunities for key processes. Improvements to the planning processes addressed inadequate integration, financial risks, lack of alternatives in evaluation of projects, and inconsistencies in spending reviews and approvals.
We developed a business requirements definition to lay out the desired end state processes. A functional and technical specification was also developed as an enterprise tool to support standardization and integration of the processes.
Results
The project resulted in vendor selection and subsequent implementation of an industry leading planning platform supporting data and process integration for the business planning cycle. The planning process improvements streamlined the efforts to identify, document, schedule and approve long range plans for each plant and presented an integrated fleet-wide plan.

Dave Thompson, Vice President
Dave is a Vice President of Financial Planning and Analysis at MCR. With over 20 years of management consulting experience to utilities, Dave has developed significant expertise in crafting innovative business solutions and sophisticated analytics in connection with strategic planning, risk management and financial planning initiatives. Dave played a key role in developing MCR’s Financial, Regulatory and Strategy Tool, which has been implemented at electric, gas and water utility IOUs, G&Ts and municipals.

Ed Schmidt, Director
Ed is a Director in MCR’s Energy Efficiency practice. He has 25 years of experience in energy efficiency and resource planning, forecasting, rates and regulation in both gas and electric utilities. His expertise includes all aspects of energy efficiency program policy, planning, program design and implementation, as well as utility regulatory policy analysis and testimony. He has presented to a variety of audiences, including The Executive Office of the President, US Department of Energy, US Environmental Protection Agency, American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy and The Energy Foundation.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Tim Schlimpert, Vice President
Tim is a Vice President at MCR and leads the Nuclear Generation practice. He has more than 30 years of utility industry experience in nuclear power plant operations, maintenance, work control, business operations, process improvement and technology solutions, and has achieved significant performance improvements for his clients. Tim provides the often elusive connection between corporate strategy, long-range planning/budgeting, work management and technology through industry-leading life cycle management practices.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Dan Rupp, Manager
With over 20 years of industry and consulting experience, Dan is a Manager at MCR. Dan transforms client financial forecasting capabilities by implementing MCR’s Financial, Regulatory and Strategy Tool and other sophisticated modeling applications. He helps provide management with insights on the impacts of alternative short- and long-term strategies and changing business and market conditions. A recognized industry expert in the area of financial and economic modeling, Dan has worked with numerous energy companies in over 30 engagements, including IOU’s, G&T’s and municipalities.

Mike Murphy, Vice President
Mike has over two decades of experience in the development and implementation of business management software, data warehousing and document management applications. As a Vice President at MCR, he designs, develops and deploys data warehouse and reporting solutions, using MCR technology and client-specified tools and technology. Mike has deep expertise in working with and implementing information systems for nuclear generation plants, including equipment reliability, system health management, work management, long range planning, budgeting and reporting.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Cindy Menhorn, Vice President
Cindy is a Vice President of Regulatory Services at MCR. She has over 35 years of experience in rates, energy efficiency, load research, revenue forecasting, cost allocation and regulatory affairs, including work on over 100 regulatory proceedings before numerous state commissions. She has directed a multifunctional rate department, managing all aspects of rate case development, including revenue requirement development, cost of service studies, revenue allocation and rate design, rate case strategy, testimony development and interrogatory response development.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Ron Kennedy, Vice President
Ron Kennedy is a Vice President with MCR. He has 20 years of experience in consulting to the utility industry. His expertise includes transmission formula rates, Section 205 rate changes, transmission rate incentives, economic evaluation of RTO membership and financial evaluation of transmission projects. Ron is experienced in presenting to executive teams and Boards of Directors.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Tom Crooks, Vice President
Tom Crooks has more than 30 years of energy industry experience and is the Vice President of MCR’s Energy Efficiency practice. Tom possesses a comprehensive understanding of the technical, financial and programmatic approaches to energy-efficiency and direct load control. Tom planned, implemented and evaluated energy efficiency programs for utilities located throughout the U.S. He has been retained by utilities, generation cooperatives, state agencies, industry associations and large end-use energy consumers located throughout North America.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile

Frank Craig, President and CEO
Frank is a co-founder and President of MCR. He has over 40 years of management consulting and business experience in the utilities industry. His has worked extensively for electric and gas utility clients advising them in areas of financial and operational processes and information systems, financial planning, budgeting, capital planning and rates and revenue requirements.
Prior to founding MCR, Frank was Senior Vice President at Utilities International, Inc., where he led the financial forecasting and modeling solutions group. Before that he was at Navigant Consulting where he specialized in facilitating management audits, improving accounting, financial and operational management processes; and implementing business management technologies. Frank began his energy career at Public Service Company of New Mexico, where he was Director of Corporate Financial Planning and Investor Relations.
Frank has authored numerous articles and white papers for Electric Light & Power Magazine and Energy Central. He holds an MBA in information technology and a BBA in finance and economics from the University of New Mexico.
![]() Visit Profile
Visit Profile
Integrating capitalization policies and units of property for a nuclear fleet merger
“The new unit of property catalogues are used daily by our accountants and engineers. The catalogues are better organized, more user friendly and are written in a language that field personnel can understand. MCR took out the confusion and created a logical, well thought out system.”
—Director, Accounting
Background
Upon completing its merger with another utility, our client needed to integrate its capitalization policies and unit of property (UoP) catalogues for its expanded nuclear fleet and overall utility property. The merger presented an opportunity to align capitalization policies, incorporate best practices and resolve previous organizational disputes. MCR had previously worked with our client on UoP catalogue integration for its merger with a former utility and was asked to assist again.
Solution
Our review of legacy UoP catalogues from both companies highlighted differences in the level of detail and component listings in multiple accounts. Functional areas became candidates for uniform application of capitalization guidance.
Referencing our capitalization best practices database of industry peers, we developed a solution to simplify the catalogue and provide more consistent guidance in classifying expenditures for capitalization. Finally, we developed an impact assessment to determine if there would be a shift between capital and O&M expense classification.
Results
The project resulted in an 80% reduction in the number of units of property. The new common units of property, along with well-defined capitalization thresholds and a user-friendly catalogue structure, simplify guidance for site organizations and reduce accounting staff time needed to analyze capital funding requests. The impact assessment estimated a minor shift in classifying expenditures from O&M to capital, easing management’s concerns about the level of capitalization in the newly merged entity.
Insights
Insights
Insights
Client Stories
Client Stories
Client Stories
What We Do
Rate Case Support and Strategy
MCR helps clients develop successful rate case strategies for state jurisdictions and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). We help evaluate the decision to file a case, define overall objectives, support the underlying rationale, prepare supporting analysis of regulatory issues, and determine the optimal timing for cases. MCR works with clients to develop a regulatory strategy that will be sustainable in the long run. We carefully examine the nature of expected short-term and long-term changes to both costs and revenues, and then we identify alternative potential regulatory strategies addressing the specific circumstances that each client faces.
Pre-Filing Review
MCR provides pre-filing reviews of regulatory petitions, pre-filed testimony, tariffs, exhibits, and minimum filing requirements before submission to regulatory commissions. MCR’s experienced professionals bring a wide variety of regulatory and ratemaking experiences; our clients benefit from our constructive reviews and recommendations on improvements to proposed filings. Conducting fully independent pre-filing reviews improves filings and builds more compelling cases for the desired regulatory outcomes.
Cost of Service Support
MCR reviews and validates your internal cost of service model to compare results and evaluate allocation methodologies for consistency with previous runs used in filed cases. Our regulatory professionals analyze allocation strategies most likely to be utilized in future rate cases or studies of alternative rate designs and make recommendations for change. For example, an existing schedule that has been active for years may need to be split into multiple schedules because the types of customers have changed over time. MCR can provide this support using results from your current cost of service model or our proprietary cost of service model COST™ In addition, MCR has developed or analyzed studies to support cost of service work, such as minimum distribution studies, lead lag studies, and depreciation study reviews.
Cost Allocation Support
MCR’s professionals have extensive experience in developing studies to allocate rate class revenue requirements and to design specific rate components. We have the capability to develop embedded and marginal class cost of service studies. We also prepare studies for revenue requirement calculations and for seasonal and time-of-use pricing. We develop sustainable solutions that adapt to changing market conditions, achieve new regulatory and pricing objectives, and match cost recovery with cost causation.
Rate Design Development
MCR works with our clients to develop regulatory filings that allow recovery of revenue requirements through a variety of traditional rate mechanisms, including modification to customer charges, evaluation of time-of-use periods, revisions to block structures, and development of other riders that recover costs of changes in infrastructure and operating costs. MCR helps clients determine the mechanisms that fit specific circumstances and develop regulatory filings based on solid justifications to support the selected approaches.
Expert Testimony Development and Review
MCR supports our clients in preparing and providing testimony; our expert contributions enable utilities to provide successful responses to regulatory participants. MCR staff have successfully testified regarding revenue requirements, cost of service, rate design, and alternative ratemaking. MCR staff have presented and supported expert testimony on behalf of clients before numerous state regulatory bodies and FERC. In addition, MCR staff have provided support to clients to ensure testimony is organized and provided in a manner consistent with regulatory requirements.
Beneficial Electrification and Revenue Enhancements
Beneficial Electrification
MCR identifies beneficial electrification opportunities and analyzes them from the perspectives of key stakeholders to assist clients in the design and eventual launch of pilots or fully scaled programs and/or products. Recognizing that various definitions of beneficial electrification exist, MCR begins with the following working definition and customizes it to frame clients’ efforts to their exact need: “Beneficial electrification is a means of powering end uses of energy with electricity; by doing so, the action must include at least two of the following without adversely affecting the others: 1) Does not negatively impact the environment and reduces GHG emissions/pollutants, 2) Saves consumers money in the long term, 3) Improves the quality of life for consumers, or 4) Provides enhanced grid management, efficiency, or other benefits.” MCR provides modeling expertise, regulatory and rate guidance, marketing channel and product delivery expertise, and guidance to balance internal and external stakeholder interests.
Revenue Enhancement
MCR works collaboratively with clients to provide customized revenue enhancement strategies, based on corporate goals and the client’s existing regulatory environment. We leverage our regulatory and financial expertise to ensure viable opportunities are offered while retaining customers and maintaining good customer experiences. MCR’s process involves facilitating client team discussions, strategically thinking through options and analyzing the viable ones; choosing the services with the greatest revenue potential; and developing a regulatory plan to gain approval for the offerings while ensuring the services align with corporate objectives. The resulting revenue enhancement strategy provides an actionable plan for our clients to achieve increased revenue opportunities.
Alternative Rate Designs, Incentives, and Cost Recovery Mechanisms
MCR uses a collaborative approach to develop specific proactive alternative rate methodologies, such as straight fixed variable rates, decoupling, weather normalization, formula rates, or multiyear rate plans, to ensure rate mechanisms reflect the operational and financial requirements of our clients. MCR creates innovative rate designs to match the unique demands of an ever-changing and evolving marketplace. We work closely with our clients to study and modify rate mechanisms to meet competitive challenges and produce desired revenue requirements.
Stakeholder Participation/Advisory Service
Working group meetings with external stakeholders can be time consuming for utility regulatory staff. MCR works collaboratively with our clients to understand their positions, thus enabling us to represent our clients’ views in working group discussions. We have successfully represented our clients at stakeholder meetings regarding a range of topics, including rate design, planning, and forecasting for energy efficiency and distributed energy.
Strategic Regulatory Analysis
Regulatory/Legislative Support and Policy Development
MCR helps our clients develop, implement, and assist with specific tasks in this process. We review and evaluate drafts of legislation and regulations and prepare comments and opinions regarding impacts on the client. MCR has advocated client interests before state regulatory commissions while coordinating regulatory efforts across corporate functions. MCR’s experiences cover a wide array of topics, such as deregulation and re-regulation drafts, Regional Transmission Organization formation, energy efficiency and demand response program development, FERC transmission issues, advanced metering, distributed generation, microgrids, and electric vehicles. MCR works collaboratively with our clients on creating policy and regulatory positions, while developing advocacy strategies that align with corporate strategies.
Rate Schedule Review
Tariff and Billing Analyses
MCR develops analyses that are based on decades of experience and industry best practices. MCR delivers analysis of each rate schedule with findings, professional insights, and actionable recommendations, all packaged in a final report, leading to improved consistency across all tariffs. When tariffs are analyzed by an independent organization, utilities gain better control over the process outside a formal rate case proceeding.
Proper Rate Schedule Determination
MCR helps interpret and develop a systematic approach to ensure our clients choose proper rate schedule determination for their commercial and industrial (C&I) customers. Through our rate option review and analysis services, we help our clients proactively provide outreach to their C&I customers, benefiting our utility clients through improved relationships with their C&I customers and regulators.
Regulatory Filing Management
Case Management
MCR facilitates the development and management of rate cases at both the state and federal levels. We provide support and guidance in overall process management, prioritize and address key issues, develop structure and strategy of supporting studies, refine testimony and exhibits, administer the flow of interrogatories and other discovery requests and responses, and manage the filing of required schedules and work papers.
Witness Training
MCR offers training courses in ratemaking, regulatory accounting, and witness effectiveness. Our Understanding Ratemaking course covers the fundamentals of ratemaking, advanced ratemaking, and contemporary topics in ratemaking. Similarly, MCR’s Regulatory Accounting class helps bridge the understanding gap between traditional GAAP and regulatory accounting requirements. Our Becoming a More Effective Witness course is customized for participants who have a role in an upcoming hearing and need to understand how to become an effective witness.
Energy Efficiency and Demand Response Regulatory Support
MCR combines its regulatory and energy efficiency experience to support our clients in these types of filings. From developing and defending load potential studies to designing programs, understanding the nuances of setting incentive levels, and applying cost-effectiveness tests, MCR professionals develop and review energy efficiency plans and create needed regulatory filings and justifications. MCR also has experience working through EM&V processes and dealing with statewide evaluators to ensure program results are presented in a manner that supports proper credit for the results achieved.
Load Forecasting Process Review
MCR works jointly with clients to assess the appropriateness of their load forecasting process and supporting models and to identify any opportunities for improvement. This analysis can include a granular review of a client’s data collection requirement or a macro-level assessment of load forecasting that ultimately supports power supply requirements. MCR’s assessment can include a benchmarking study that provides our clients meaningful comparisons to their peers.
MCR Models
COST™
MCR’s Cost of Service Toolis ideal for regulatory professionals seeking to provide greater transparency to regulators, intervenors, and other stakeholders. The tool provides full functionality to design rates for rate case filings as well as typical bill analysis. Built by regulatory professionals in Microsoft Excel, COST™ is a fully functional cost of service model with open logic for audit, review, scenario analysis, and user editing. It allows for development of the cost of service without any buried code or time-consuming run-time macros. New cost elements, revenues, or rate base items can be quickly integrated into the analysis; adding new rate schedules is as simple as inserting a column into Excel. Learn more by downloading a COST™ brochure and reading about five features a cost of service model must have. Upon request, MCR experts will facilitate a live, online demonstration of COST™ and will answer your questions during the meeting. Contact us for more information.
Rate Design Module (included in COST™)
MCR’s rate design module connects seamlessly with the COST™ model. Rate schedule revenue requirements are imported from the client’s cost of service model, and rate design personnel can choose to manually adjust the proposed rate increase for each class or have the model run the calculations. MCR provides additional rate design support in conjunction with and separate from this model.
Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™)
Is a sophisticated planning tool that is easy to operate without the software coding and expense of proprietary “black box” models on the market. FRST™ has a unique approach to regulatory analysis, allowing a high degree of flexibility. The model calculates revenue requirements based on key drivers and identifies the need for potential revenue changes. The easy-to-use regulatory planning panel allows for historic and future test years with movable test periods and rate effective dates. Analysts can quickly adjust rate base, costs, and revenues based on the most recent rate case or test new assumptions.
FRST™ is written in Excel with a unique structure that manages large amounts of data, yet requires no coding, and allows users to quickly change the model’s logic and reports to address changing business needs. With its flexible data loading and mapping function, users can easily load data from budgeting, general ledger, and capital asset systems. FRST™ seamlessly integrates with production cost and gas supply planning models.
What We Do
Strategy and Stakeholder Engagement
Internal strategy development and execution
MCR recognizes energy efficiency (EE) is no longer simply a compliance obligation, but rather is part of broader strategic efforts in grid modernization, distributed energy resources (DER) and customer engagement. MCR brings together internal functional areas that are affected directly or influenced indirectly by EE operations and regulation to ensure awareness and alignment. Together, we facilitate development of internal EE strategies that are complementary to and consistent with what have traditionally been core business strategies, and assist in development and execution of tactical plans.
Stakeholder strategy and engagement
MCR identifies areas where policy/regulatory activity explicitly related to EE affects other functional areas and where such activity affects EE. We weave together these political and regulatory agendas and facilitate development of external EE strategies and tactical execution plans that are aligned with and support non-EE functional areas. We support execution by providing issues analysis and assisting with relationship management with regulators, key customers, EM&V evaluators, consumer groups and other stakeholders.
Program Planning and Design
Program Planning
MCR develops forecasts of technical, economic and achievable energy efficiency potential. Our approach to such work is distinct in that it is transparent, not wholly reliant on the federal energy surveys (RECS, CBECS and MECS), and includes primary research to accurately segment and describe client markets. Our approach is also comprehensive in that it includes consideration of DR and DER. Importantly, when we forecast potential, we do so with explicit consideration of segment-specific measures, not simply segments and end-uses.
Program design
MCR achieves energy efficiency potential, whether the underlying potential study is developed by us or otherwise, by designing programs with proven market segment-driven delivery channels and by comprehensively incorporating current technologies and practices. We constantly ask the question, “What does the data tell us this market segment needs?” rather than simply tweak existing program designs without consideration of their going-forward relevance and effectiveness. All of our program designs are carefully thought out from a process and data perspective in light of our commitment to the principle that programs designed to be measured measure well.
Pilots and innovation
MCR sees the rapid evolution of technology and customer desires and preferences as an opportunity for, not as a threat to utilities and their EE programs. To that end, we develop and either implement directly or coordinate implementation of programs, and provide measurement and reporting of pilot programs and data or administrative innovation. Examples include pioneering work on optimizing water and energy efficiency, geotargeting of EE programs to provide non-wires relief to distribution systems and use of battery storage as a peak (and thus total resource cost) mitigation tool. Our work on data management and modeling and analysis of advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) data is cutting edge.
Program implementation
Program management and oversight
MCR provides overall program management and oversight of third-party implementation vendors. Our program implementation services include developing RFPs and contractor statements of work, then staying engaged in procurement through proposal review, vendor selection, and contracting. We perform quality assurance functions to include project review, site verifications and preparation of responses to evaluator data requests and/or rebuttal of critical findings when warranted.
Project development
MCR develops site-specific, engineering-based energy efficiency projects, often pursuant to memoranda of understanding directly between our utility clients and their largest customers. The projects include retro-commissioning of municipal, university, primary and secondary education, and healthcare facilities. Sometimes, these projects take the form of public agency partnerships where our utility clients partner with local governmental organizations to undertake high-value energy efficiency projects.
Independent Evaluation of EE Implementation Solicitations
Energy Efficiency Operational, Technical and Regulatory Support
Energy Utility Offerings
Energy utilities must obtain adequate responses to implementation solicitations (RFI/RFA/RFP, etc.), qualify would-be implementers, perform proposal scoring and vendor selection, convert provider proposals into contract statements of work and then present their contracts for regulatory approval. MCR can assist utility program sponsors in navigating contracting challenges and regulatory hurdles by relieving general purchasing staff and over-burdened energy efficiency department staff from performing these specialized tasks. Services include drafting solicitation releases, facilitating bidder conferences, developing scoring criteria, training utility staff proposal evaluators, conducting scoring, creating selection criteria, facilitating scoring calibration, recording and required regulatory reporting of selection results.
State Regulator Offerings
State regulators must oversee utility solicitation processes to ensure objective and unbiased use of ratepayer funds for hundreds of millions of dollars in energy efficiency programming annually. They need qualified, independent and objective oversight from technical experts who can review the entire utility solicitation process and serve as a consultant to the regulatory commission. As an independent evaluator, MCR performs detailed reviews of solicitation document development by utilities, monitors all bidder communications, evaluates and shadow scores all bidder responses, analyzes all data and workpapers, provides recommendations to the utility and regulators throughout the solicitation, observes contract negotiations and selection discussions, analyzes bidder implementation plans and reports on all findings. MCR’s review is used to inform the regulatory oversight.
Client Stories
The Growing Imperative for Natural Gas Energy Efficiency – American Gas Foundation
The American Gas Foundation (AGF) engaged MCR to evaluate the full range of current and future potential benefits that could accrue from natural gas utility energy efficiency (EE) programs, including 1) the current state of gas utility EE cost-effectiveness, and 2) perspective potential future benefits. The report provides an in-depth survey of existing natural gas utility EE programs as well as potential future program approaches and incentive strategies. The study also highlights opportunities to leverage indirect and non-energy benefits stemming from optimal and efficient use of natural gas delivery infrastructure.
Optimizing capital spending for a large nuclear fleet
“Over the past seven years, we have formalized a process around using the MCR project evaluation methodology and tools, and have applied it to our entire fleet.”
—Manager, Project Evaluation
Background
A large utility in the south had a strategic objective of becoming the best managed nuclear fleet in the nation as measured by its ability to achieve a rank of first or second among all US nuclear fleets in key performance indicators. The company’s nuclear organization identified the business case evaluation of major projects, to align safety and reliability with cost, as a cornerstone to achieve the strategic objective. The nuclear organization recognized MCR’s unique approach to developing business cases as a best practice and asked us to work with their staff for implementation.
Solution
We worked with our client’s engineering and business personnel to develop business cases for selected projects. Each business case identified alternatives and quantified risk through sensitivity, breakeven and probabilistic risk analysis. A key measure of success was the development of robust project alternatives with dollar and percentage savings from the baseline budget for the selected projects.
Results
Coordinating with our client’s staff, we developed 10 business cases and provided “hands-on” training on the approach. We created a desktop evaluation guide to document the business case process and to institutionalize the approach.
The 10 business cases resulted in savings of more than 20% of the original budgeted amounts, exceeding our client’s investment in the project by a factor of 40x.
Insights
Determining and managing long-term costs and reliability with life cycle management plans for a nuclear operation in the south
Background
A large utility in the south operates a fleet of three nuclear plants that were facing uncertain future investment requirements. The company’s management was challenged by the organization’s limitations in planning for major projects beyond a one-year horizon.
Knowing that they were facing long-term maintenance, reliability and cost issues, a more comprehensive approach using life cycle management plans (LCM) was needed. The company decided to develop LCM plans for key plant systems across the nuclear fleet and chose MCR to help.
Solution
MCR worked with our client’s engineering staff to identify key plant systems to develop LCM plans. We conducted extensive external research using industry reliability data, operating experience, NRC documents and equipment vendor sources to identify potential LCM issues. Using internal research, we analyzed data from the client’s work management system to identify additional LCM issues specific to the plants.
The results of the research allowed us to identify reliability issues with higher risk components, and these became the basis for recommendations around future maintenance. The existing and recommended maintenance initiatives were consolidated to produce a comprehensive document and project plan for each system with scope, schedule and cost to end of plant life.
Results
The project provided our client with documentation of the analysis approach and results. The resulting LCM plans included end of life work plans and funding requirements for each system. Implementation of the LCM plans will help our client attain safety and reliability objectives while optimizing expense and capital investments.
What We Do
Transmission Formula Rate Analysis
Formula rate review for existing transmission owners
MCR conducts reviews of transmission formula rates, (MISO Attach. O, & SPP/PJM Attach. H) to substantiate costs and optimize revenue.
Development of annual transmission revenue requirements (“ATRR”) for new transmission owners
MCR develops cost data to support full RTO revenue recovery for new transmission owners (“TOs”), which involves, for example, developing MISO’s Attachment O, and Attachment H in SPP and PJM. In addition, MCR develops and reviews client updates to annual formula rates and defends client updates against challenges from neighboring utilities, as appropriate.
Review/Challenge to incumbent formula rate costs
MCR reviews neighboring utility transmission costs or RTO cost calculations to ensure transmission charges are appropriate.
Staff education workshops on formula rates
MCR conducts workshops to educate client staff on formula rates and the implications of business changes on ATRR.
FERC Filings
Section 205 rate filings and testimony
MCR provides expert FERC testimony for Section 205 rate filings, including new ATRR filings related to joining an RTO. Our expertise includes testimony and formula rate template development/changes.
Transmission incentive rate filings and testimony
MCR provides analytics, formula rates and testimony for transmission incentives rate applications to FERC. This includes requests for hypothetical capital structure, CWIP, abandoned plant and regulatory asset.
Cost of capital expert testimony
MCR provides expert testimony and analytics to support proposed cost of capital for new and existing formula rates for public power and cooperatives, including margin requirement, ROE and capital structure.
Intervention and settlement support
MCR provides our clients analytical and intervention response support during intervention, settlement, mediation and hearings.
James Pardikes Direct FERC Testimony Experience
James Pardikes Experience Statement
Strategic Economic Analysis
Development of transmission business plans
MCR works with clients to define transmission business plans that lead to running transmission as a business. This work includes identifying transmission-related issues, developing strategies to address priority issues, and identifying transmission projects, including providing analytic/economic support for proposed projects.
Economic evaluation of new transmission projects
MCR analyzes cash flows of proposed transmission projects. MCR’s Transmission Project Evaluation Tool™ highlights how value is created under various cost allocation and recovery scenarios and helps prioritize capital.
RTO membership evaluations
MCR conducts economic analysis using MCR’s RTO Evaluation Model™ to assess whether to become a transmission owner in an RTO.
Analysis of joint zone investment and 7-factor tests
MCR provides analytical support in negotiations with incumbents on the appropriate share of eligible transmission investment in a joint pricing zone. In addition, MCR works with our clients to assess the eligibility of their transmission assets under RTO tariffs, including conducting analyses under the FERC 7-factor test.
Analysis of the potential purchase or sale of assets
MCR conducts strategic and financial analysis related to value created from buying or selling transmission facilities. MCR provides various valuation techniques to assess the market value of transmission assets under various market/competitive environments.
Transmission Cost/Rate Competitiveness
Peer cost comparison by FERC account
MCR conducts transmission cost comparisons with peer utilities by FERC account for transmission owners to identify potential areas warranting cost reduction and/or differences in the recording of costs.
Rate strategy and transmission revenue forecasting
MCR develops forecasts of ATRR and transmission rates for its clients to assess their rate competitiveness and better understand the levers to manage future rate increases. ATRR forecasts are developed under various transmission investment scenarios. Analyses also include evaluating generator interconnection investment options such as utility-funded and customer-funded investment.
Transmission capital investment and metric comparisons
MCR maintains a proprietary database of transmission capital investment, load and comparative cost metrics for TOs and industry segments in various RTOs. This information provides analytical support in cost competitive analyses, MCR expert testimony in FERC filings and in negotiations with incumbents on the appropriate share of transmission investment in a joint pricing zone.
What We Do
Financial forecasting
MCR helps our clients develop financial plans, evaluate strategies, quantify risks and manage cash flow through our Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™), the only financial forecasting solution in the utility industry.
Regulatory analysis
MCR’s Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™) provides in-depth analysis of revenue requirements and provides regulatory groups with insights on potential needs to adjust rates. FRST™ can be linked to MCR’s Cost of Service Tool (COST™) and rate design module, providing a full range of products for regulatory professionals.
Enterprise risk management
MCR conducts enterprise risk management diagnostics to provide a comprehensive understanding of a company’s current ability to identify and manage risks. Using Monte Carlo simulation tools combined with MCR’s Financial and Regulatory Strategy Tool (FRST™), we quantify risks and incorporate our calculations into financial forecasts of earnings and cash flow.
Strategic planning
MCR engages client teams to set strategic direction, develop operational plans and create meaningful performance metrics and targets. Our data-driven analytic approach helps our clients understand the key issues they face and assess their potential strategic options.
Capital allocation
MCR evaluates capital projects using a risk-based approach to assess multiple alternatives and provide objective insights into the best option. We engage middle and senior management teams in the process of determining the optimal portfolio of capital projects.
Contact
Thank you for your interest in MCR. Our address is:
MCR Performance Solutions
155 N. Pfingsten Road
Suite 155
Deerfield, IL 60015
Phone: 847-562-0066
Fax: 847-562-0077
Careers
As a knowledge-based consulting firm, MCR’s success is driven by the quality of our staff. That’s why we work hard to build teams of experts, finding just the right people to ensure we deliver exceptional results for our clients.
A career at MCR means accepting a wide variety of responsibilities and delivering top-notch results to our clients. Anticipate a rapid integration into our firm and our work. Be ready to jump right in with your expertise and knowledge. Expect to be challenged.
Our Company
MCR is a management consulting firm specializing in the energy industry. We work on many types of assignments, but all share the same objective: to help transform our clients’ performance. We work on projects to improve our clients’ strategies, operations, processes, finances, forecasting, organizational designs, economics, testimony, and business cases. Our practice areas include Financial Planning and Analysis, Regulatory Services, Energy Products and Services, Transmission Strategy, Nuclear Generation, and Strategic and Financial Advisory.
Our Staff
MCR’s staff is a group of highly motivated professionals exhibiting intellectual curiosity and displaying a drive to develop creative solutions to challenging business issues. Our team leverages a solid foundation of deep knowledge, insights, and experience in all aspects of the energy industry.
Our Culture
When you join MCR, you will have opportunities to work with, learn from, and grow alongside all levels of our staff, within MCR and at our client sites. Regardless of project location or type of assignment, MCR leaders and staff remain true to our core values:
- Intellectual Capital. Achieving a deep understanding of the energy industry and the possibilities inherent in creating operational excellence
- Market Presence. Delivering to the marketplace the MCR message, “We will transform the performance of our clients, making a real difference for our clients and the industry”
- Quality. Providing the highest-quality deliverables possible to our clients
- Innovation. Pushing our staff and our clients to raise their ambition and continually reach for the next level of achievement
- Commitment and Accountability. Taking personal initiative to make MCR a successful and enjoyable place to work
- Teamwork. Collaborating with each other and with our clients to produce results
Our Advantage
MCR is a boutique consulting firm offering unique benefits to our staff. Our consultants have told us they chose MCR for our:
- Collegial Atmosphere. From drafting white papers to forging new business relationships, developing proposals to executing client projects, we all work together toward successful outcomes.
- Autonomy. MCR leaders don’t micromanage; they encourage you to create your own winning solutions.
- Variety. Each project is different from the one before it. Even with assignments that have a similar focus, each client brings a different mix of challenges, capabilities, and personalities.
- Responsibility. In a small company, everyone is responsible for delivering a high-quality work product, which means consultants may have multiple roles on any given project.
- Exposure. New consultants work with and learn from high-level management, and seasoned team members have the opportunity to guide and advise those newer to the utility consulting industry.
- Making a Difference. From finding significant savings to analyzing and resolving complex issues, our consultants deliver significant value to our clients and, ultimately, to the customers they serve.
Join Our Team!
If you’re interested in joining the MCR team, please send your resume to Carolyn Duffley at cduffley@mcr-group.com.
MCR Team
About Us
We are proud of our firm’s achievements. We measure our firm’s success from the perspective of our clients. They want to work with a firm that is exceptional in the areas of:
- Client Relationships. We have built long-term relationships with our clients spanning two decades. Over 90% of our business is from our existing clients, whom continue to hire us to develop solutions to their critical economic and strategic business challenges.
- Value Creation. We have created hundreds of millions of dollars in value for our clients through our consulting assignments. That value is measured by the costs we have reduced, the new revenue we have added and the energy we have saved for our clients and their customers.
- Reputation. We have developed an excellent reputation with our clients and throughout our industry. Our reputation is based on the quality of our work and the unique value proposition we provide to our clients. We measure the quality of our reputation through our Client Stories and what they tell us about the service and value we provide for them.
We are continually excited about the opportunities we see in the industry and our prospects for building significant value for our clients.
Client Stories
Insights
What We Do
Risk informed budgeting
MCR reduces and controls O&M costs by working with budget owners to justify all budget expenditures from a baseline of zero. We risk-rank every budget line item by evaluating the risk incurred if not funded and then comparing risk in the context of complete budgets. Our “challenge process” uses a peer review method to assess each budget line item and determine the ability to adjust the amount and timing of each expenditure.
Click here to read our client story, Achieving cost reduction through risk informed budgeting for a top-10 municipal utility.
Process improvement
MCR’s approach to process improvement models core processes for the entire organization. We model core processes, such as equipment reliability, work management and business planning, to a detailed, individual contributor level, where every process step, hand-off and deliverable are documented in a work breakdown structure format. Every process step, as well as every organization’s participation within the step, is evaluated and scored, allowing a rollup of performance valuations. The rollups then allow drilldowns from high-level processes or organizations to identify where processes and organizations need improvement.
Capital portfolio optimization
MCR’s consultants analyze existing capital plans and apply a short-form business case approach for every proposed project. This enables a risk valuation for every project to contrast against proposed investments. MCR’s Portfolio Dashboard summarizes the effectiveness of portfolio investments and identifies opportunities to reduce, delay or reallocate capital funding.
Capitalization policies and procedures
MCR experts review, analyze and benchmark capitalization policies to ensure management is capitalizing all allowable costs. We also assess the retirement unit catalog and make recommendations for additions, deletions, or modifications to ensure the catalog is aligned to the most recent industry capitalization practices. The MCR unit of property catalog and database provide clear capitalization guidance, which reduce staff time spent on analyzing capital funding requests.
Read our related client stories:
- Updating a unit of property catalogue for a government utility
- Integrating capitalization policies and units of property for a nuclear fleet merger
Capital project evaluation
MCR optimizes capital project spending by developing robust business cases with creative alternatives and quantifying reliability and safety risk. Our exhaustive research to determine equipment failure probabilities combined with consequence scenarios allow us to correctly value project alternatives when considering investments to avoid equipment failure. We also establish and facilitate a client Executive Review Team to review the business cases and make the final spending decisions.
Click here to read our client story, Optimizing capital spending for a large nuclear fleet.
Life cycle management planning
MCR’s experts develop life cycle management (LCM) plans, which help maintain the long-term health of key plant systems. We accomplish the complete discovery of the “known or knowable” issues surrounding equipment to ensure our plans are complete and without surprises. The plans improve management’s ability to achieve safety and reliability objectives, while optimizing long-term expenses and instilling confidence in the capital plan.
Click here to read our client story, Determining and managing long-term costs and reliability with life cycle management plans for a nuclear operation in the south.
Long range planning
MCR develops and implements strategies for improving long range planning processes and supporting information systems with a focus on equipment reliability, work force planning, outage planning and budgeting. The implemented processes ensure equipment reliability processes are integrated with work management, business planning, budgeting and staffing processes.
Click here to read our client story, Improving long range planning processes and systems for the operator of a large nuclear fleet.
Management reporting
MCR develops and implements improvements to management reporting processes and reporting systems to provide management with greater visibility and understanding of O&M, capital and outage costs, and cost drivers. In every case, we focus on creating views with actionable information and a focus on ownership and accountability.
Staffing optimization
Often conducted in concert with risk-informed zero-base budgeting, MCR conducts a detailed task analysis for every staffing resource to determine the criticality and risk-rank for every task across the organization. We create consolidated profiles across the organization to determine where staffing resource opportunities lie. This information is then used to create a staffing optimization plan incorporating expected attrition for integration with the risk-informed budget.
Click here to read our client story, Creating significant cost reductions at a Pacific Northwest generating station.
Implementation of Copperleaf Suite of asset optimization tools
MCR works with Copperleaf Technologies and large utilities to implement the Copperleaf Suite of asset optimization tools:
- Copperleaf Asset: Forecast sustainment needs and manage risk and manage risk in your critical infrastructure
- Copperleaf Portfolio: Make the highest value decisions and create the optimal investment strategy
- Copperleaf Value: Increase business agility and transparency across the enterprise
MCR’s implementation roles include data conversion and integration, reporting, training, and value framework application to investment request valuations. We apply our deep utility experience and asset specific knowledge to integrate business case development with Copperleaf value frameworks. We work directly with utility clients and Copperleaf Technologies from kickoff through implementation and rollout to users to sustained use by clients.
Click here to read our client story, Achieving optimized funding through a value-based decision-making process.
Home
Transforming utility company performance through deep industry insights and innovative solutions
MCR is a management consulting firm serving the utilities industry. We are different because we focus on just a few of the critical issues that electric, natural gas and water companies face. Today these issues surround the need to find new opportunities in changing markets, develop new sources of revenue, manage risk, control costs, and achieve fair treatment in the regulatory process.
For over 25 years we have delivered exceptional results for utilities. Our clients tell us that they hire MCR for three principal reasons:
- We provide expertise that is hard to find elsewhere
- We deliver measurable results on every project
- We are easy to work with
 Our consulting experts possess deep industry knowledge and are dedicated to the relentless pursuit of creating value for our clients. We bring together teams of our experts to deliver client work and our senior practice leaders are actively involved in every project.
Our consulting experts possess deep industry knowledge and are dedicated to the relentless pursuit of creating value for our clients. We bring together teams of our experts to deliver client work and our senior practice leaders are actively involved in every project.
This is who we are and why we are successful.
Frank Craig
President and CEO
Transmission Strategy
MCR does consulting work in various regional transmission organizations (“RTOs”), including MISO, SPP, PJM, CAISO and NYISO. Our clients—G&T cooperatives, municipals, joint action agencies, public power districts and independent transmission developers—have a goal of optimizing the value of their current and future investments in electric transmission. We help them realize the full revenue potential from their transmission assets.
Through our consulting assignments, we have created millions of dollars in value for our clients and broken new regulatory ground for our client base with landmark decisions in FERC rulings.